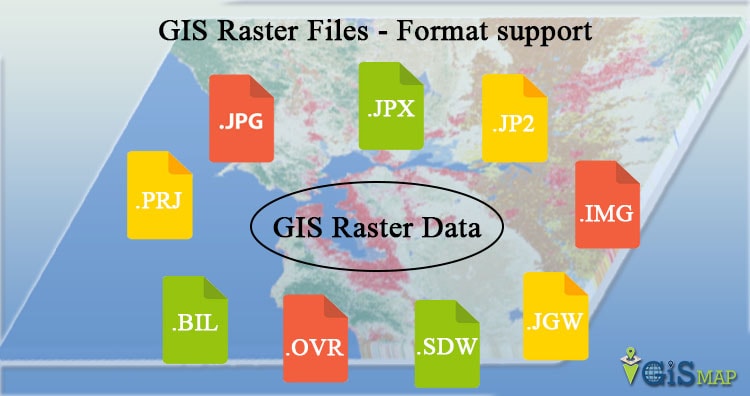
Digital raster graphic(DRG)
Digital Raster Graphic is a raster file format. From scanning a paper USGS topographic map for use on a computer a digital image is created called DRGs. The DRGs which are created by USGS are typically scanned at 250 dpi and then the DRGs are saved as a TIFF file in the server. The Raster data image usually includes the original border information, referred to as the “map collar”. The raster map file is projected by UTM and georeferenced to the surface of the earth.
ARC Digitized Raster Graphic (ADRG)
ARC Digitized Raster Graphics is a standard National Imagery and Mapping Agency (NIMA) digital product. ADRG is designed to support applications that require a raster map background display.
ADRGs are the digitized maps and transformed charts and The intended exchange medium for ADRG is a compact disk (CD-ROM)
The ADRG’s charts transformed into a specific georegistration framework and acccomplnied by ASCII encoded support files. ADRG is geographically referenced using the equal arc-second raster chart/map (ARC) system in which the globe is divided into 18 latitudinal bands, or zones. The data consists of raster images and other graphics generated by scanning source documents.
Multiple files
Data file—extension *.img or *.ovr
Legend file—extension *.lgg
Enhanced Compressed ARC Raster Graphics (ECRG)
Enhanced Compressed ARC Raster Graphics (ECRG) file is an Enhanced Compressed ARC Raster Graphics. ECRG is geographically referenced using the ARC system in which the globe is divided into 18 latitudinal bands, or zones. ECRG uses JPEG 2000 compression.
Distributed by the NGA. CADRG/ECRG is geographically referenced using the ARC system. The data consists of raster images and other graphics generated by scanning source documents. CADRG achieves a nominal compression ratio of 55:1. ECRG uses JPEG 2000 compression using a compression ratio of 20:1
Compressed ARC Digitized Raster Graphics (CADRG)
CADRG is a comprising computer-readable digital map and chart images. they are also the file formats of Raster data. CADRG files are usually physically formatted within a National Imagery Transmission Format (NITF) message. It supports various weapons, C3I theater battle management, mission planning, and digital moving map systems. CADRG data is derived directly from ADRG and other digital sources through downsampling, filtering, compression, and reformatting to the Raster Product Format (RPF) Standard.The CADRG Reader can read CADRG files with or without the NITF message wrapper. The CADRG Writer can create CADRG datasets with or without the NITF message wrapper.
CADRG achieves a nominal compression ratio of 55:1. ECRG uses JPEG 2000 compression using a compression ratio of 20:1
File extension is based on specific product. You can specify which products you want ArcGIS to recognize (Customize > ArcMap Options > Raster > File Formats).
Raster Product Format (RPF)
Raster Product Format, military file format specified in MIL-STD-2411. RPF is a standard data structure developed in 1994 as a U.S. Military Standard for geospatial databases. RPF’s database is composed of rectangular arrays of pixel values (e.g. in digitized maps or images) in compressed or uncompressed form.
It was designed as a adaptable format to encompass raster data products in compressed or uncompressed form. The intent was to enable application software to use the data in RPF format on computer readable interchange media (e.g. CD-ROM) directly without further manipulations or transformation.
The underlying format of CADRG and CIB.
Single file—no standard file extension
1. Compressed ADRG – Compressed ADRG, developed by NGA, nominal compression of 55:1 over ADRG (type of Raster Product Format)
2. CIB – Controlled Image Base, developed by NGA (type of Raster Product Format)
Binary file
An unformatted file consisting of raster data written in one of several data types, where multiple band are stored in BSQ (band sequential), BIP (band interleaved by pixel) or BIL (band interleaved by line). Georeferencing and other metadata are stored one or more sidecar files.
The Binary Terrain format was created by the Virtual Terrain Project (VTP) to store elevation data in a more flexible file format. The BT format is flexible in terms of file size and spatial reference system.
Single file—extension *.bt
Projection file—extension *.prj
Enhanced Compressed Wavelet (ECW)
A compressed wavelet format, often lossy. ECW is a proprietary format of ERMapper for imagery compression. It is a more recent format than MrSID, but is gaining popularity because of free compression utilities available from ER Mapper’s website. ECW is a propriatary format. It is a wavelet-based, lossy compression, similar to JPEG 2000.
It is a proprietary wavelet compression image format optimized for aerial and satellite imagery.
This format can be used for Desktop, but when publishing, you require the ECW for ArcGIS for Server extension license.
Single file—extension *.ecw
ESRI grid – proprietary binary and metadataless ASCII raster formats used by Esri. A proprietary Esriformat that supports 32-bit integer and 32-bit floating-point raster grids. Grids are useful for representing geographic phenomena that vary continuously over space and for performing spatial modeling and analysis of flows, trends, and surfaces such as hydrology.
color map file—extension *.cl
Extensible N-Dimensional Data Format(NDF)
Format used for storing data representing n-dimensional arrays of numbers, such as images. Uses container files (directories containing files and directories) to manage the data objects.
Directory—extension *.sdf
GDAL Virtual Format (VRT)
This is a file format created by the Geospatial Data Abstraction Library (GDAL). It allows a virtual dataset to be derived from other datasets that GDAL can read.
Single file—extension *.vrt
Tagged Image File Formats (TIFF)
This format is associated with scanners. It saves the scanned images and reads them. TIFF can use run length and other image compression schemes. It is not limited to 256 colors like a GIF. Widespread use in the desktop publishing world. It serves as an interface to several scanners and graphic arts packages. TIFF supports black-and-white, grayscale, pseudo color, and true color images, all of which can be stored in a compressed or decompressed format.
BigTIFF is supported.
Single file — possible file extensions *.tif, *.tiff, and *.tff
World file — extension *.tfw
ArcCatalog only recognizes the .tif file extension by default. To add .tiff or .tff files to ArcMap without renaming them, add those file extensions to ArcCatalog or drag those files from Windows Explorer into your map.
Geo Tagged Image File Formats (GeoTIFF)
TIFF variant enriched with GIS relevant metadata, As part of a header in a TIFF format it puts Lat/Long at the edges of the pixels. GeoTIFF driver supports reading, creation and update of internal overviews. Internal overviews can be created on GeoTIFF files opened in update mode (with gdaladdo for instance). If the GeoTIFF file is opened as read only, the creation of overviews will be done in an external .ovr file. Overview are only updated on request with the BuildOverviews() method. The GeoTIFF format is fully compliant with TIFF 6.0, so software incapable of reading and interpreting the specialized metadata will still be able to open a GeoTIFF format file.
Graphic Interchange Format (GIF)
Graphic Interchange Format. A file format for image files, commonly used on the Internet. It is well-suited for images with sharp edges and relatively few gradations of color. A bitmap image format generally used for small images.
Single file—extension *.gif
World file—extension *.gfw
Digital Elevation Model (DEM)
The representation of continuous elevation values over a topographic surface by a regular array of z-values, referenced to a common vertical datum. DEM is sometimes used as a generic term for DSMs and DTMs, only when DEM representing height information without any further definition about the surface.
A DEM can be represented as a raster data(a grid of squares, also known as a heightmap when representing elevation) or as a vector-based triangular irregular network (TIN). When you look at a Digital Elevation Model (DEM) on a map, you don’t see a cell matrix. Instead, you see a layer symbolized by a color ramp.
- Digital Elevation Models or DEM have two types of displays
The first is 30-meter elevation data from 1:24,000 seven-and-a-half minute quadrangle map. The second is the 1:250,000 3 arc-second digital terrain data. DEMs are produced by the National Mapping Division of USGS.
- Spatial Data Transfer Standard (SDTS) digital elevation model (DEM)
The Spatial Data Transfer Standard (SDTS) was created by the USGS. The purpose of this format was to transfer digital geospatial data between various computer systems in a compatible format that would not lose any information.Multiple files—extension *.ddf
The actual elevation file that ArcGIS reads is named *CATD.DDF.
- United States Geological Survey (USGS) digital elevation model (DEM)
This format consists of a raster grid of regularly spaced elevation values derived from the USGS topographic map series. In their native format, they are written as ANSI-standard ASCII characters in fixed-block format.Single file—extension *.dem (need to change .dat extension to .dem)
RS Landsat
Landsat satellite imagery and BIL information are used in RS Landsat. In one format, using BIL, pixel values from each band are pulled out and combined. Programs that use this kind of information include IDRISI, GRASS, and MapFactory. It is fairly easy to exchange information from within these raster formats.
ArcInfo Grid
An ArcInfo Grid does not have an individual file extension. Instead it is composed of two folders within a “workspace” which each contain multiple files. One of the two folders carries the name of the grid, and contains a number of various .adf files. The other folder is an “info” folder, which typically contains .dat and .nit files for all the coverages and grids in the workspace. The best way to manage (copy, move, delete, rename) ArcInfo Grids is with ArcCatalog or ArcInfo Workstation (command line).
Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AIRSAR) Polarimetric
AIRSAR is an instrument designed and managed by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). ArcGIS supports the polarimetric AIRSAR data (POLSAR).
Multiple files with an L, C, or P in the file name followed by .dat. For example: mission_l.dat (L-Band) and mission_c.dat (C-Band).