Haversine Formula – Calculate geographic distance on earth. If you have two different latitude – longitude values of two different point on earth, then with the help of Haversine Formula, you can easily compute the great-circle distance (The shortest distance between two points on the surface of a Sphere). The term Haversine was coined by Prof. James Inman in 1835. Haversine is very popular and frequently used formula when developing a GIS (Geographic Information System) application or analyzing path and fields.
You can use this Online Route Compass Tool, which calculates the distance based on haversine Formula and also computes the Bearing angle too :
Route Compass Online Tool to Compute Haversine Distance

Haversine formula:
Central angle Haversine can be computed, between two points with r as radius of earth, d as the distance between two points, 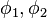 is latitude of two points and
is latitude of two points and  is longitude of two points respectively, as:
is longitude of two points respectively, as:
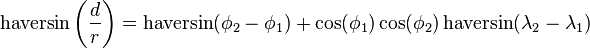
Law of Haversine:
To derive law of Haversine one needs to start the calculation with spherical law of cosine i.e cos a = cos b * cos c + sin b * sin c * cos A
One can derive Haversine formula to calculate distance between two as:
a = sin²(ΔlatDifference/2) + cos(lat1).cos(lt2).sin²(ΔlonDifference/2)
c = 2.atan2(√a, √(1−a))
d = R.c
where,
ΔlatDifference = lat1 – lat2 (difference of latitude)
ΔlonDifference = lon1 – lon2 (difference of longitude)
R is radius of earth i.e 6371 KM or 3961 miles
and d is the distance computed between two points.
Here is the example result delivered by Haversine Formula:
Lets take one of latitude-longitude for calculation distance,
NEBRASKA, USA (Latitude : 41.507483, longitude : -99.436554) and
KANSAS, USA (Latitude : 38.504048, Longitude : -98.315949)
Do compute the distance with the above written formula. Your answer would be 347.3 Km(kilo-meter). The snapshot demonstrate the same result with map below.

- You can also find the Tool to calculate the distance between two points on earth and display on Google map.
- Also do see the tutorial for how to make your own customization Google map.
- You can also check for JavaScript code for Haversine formula.
- Google Map Straight line distance calculation feature
If you are getting problem in understanding Haversine formula or getting error in the result do comment below. Also if you have more relevant information about the same, do share with us by writing below.
Thank you for the great website.
How much error is generated in the bearing calculation as a result of using an average radius of the earth? For coordinates separated by no more than 500 miles, is the Haversine formula the best?
Thank you,
Gary
Does anyone have the work shown to further understand the process of navigating these formulas? I’m at a standstill after trying to solve for c.
A submarine cable will be extended between two cities I and J that located on both sides of a sea and have the following geodetic coordinates: I (34°55´N, 56°10´E) J (33°56´N, 130°48´E) R = 3671 km.
i) The minimum cable length in kilometers. 5
ii) The direction or azimuth that should be extended this cable from point I.
The format for atan2 function in excel is atan2(y,x). So instead of (√a, √(1−a)) it will be (√(1−a),√a)
For excel users, to save you the headache:
a = (SIN((RADIANS(Lat2-Lat1))/2)^2)+(COS(RADIANS(Lat1))*COS(RADIANS(Lat2))*SIN((RADIANS(Lon2-Lon1))/2)^2)
c =2*(ATAN2(SQRT(RADIANS(a)),SQRT(1-RADIANS(a))))
d = 6371*RADIANS(D15)