File conversion is an essential step in the GIS process that ensures the easy use of GIS data in various applications. A popular GIS format for displaying geographic features including points, lines, and polygons is SHP. Working with MapInfo GIS software requires the use of MID.
What is SHP File?
In GIS, a popular geographic vector data format is a SHP file (Shapefile). For spatial characteristics, it saves the attribute data—descriptive information—and geometry—points, lines, and polygons. SHP files are compatible with applications such as ArcGIS and QGIS, and are frequently used for mapping locations, boundaries, and other geographic data. In order to store associated data, they frequently come with extra files.
Key Concept for Conversion SHP TO MID:
MAPOG‘s Converter Tool offers a user-friendly platform for converting data between various formats. Its intuitive interface ensures users can complete the conversion process efficiently. Here’s a step-by-step guide on converting SHP files to MID format using MAPOG.
Step-by-Step Guide to Converting SHP to MID
Step 1: Upload the Data
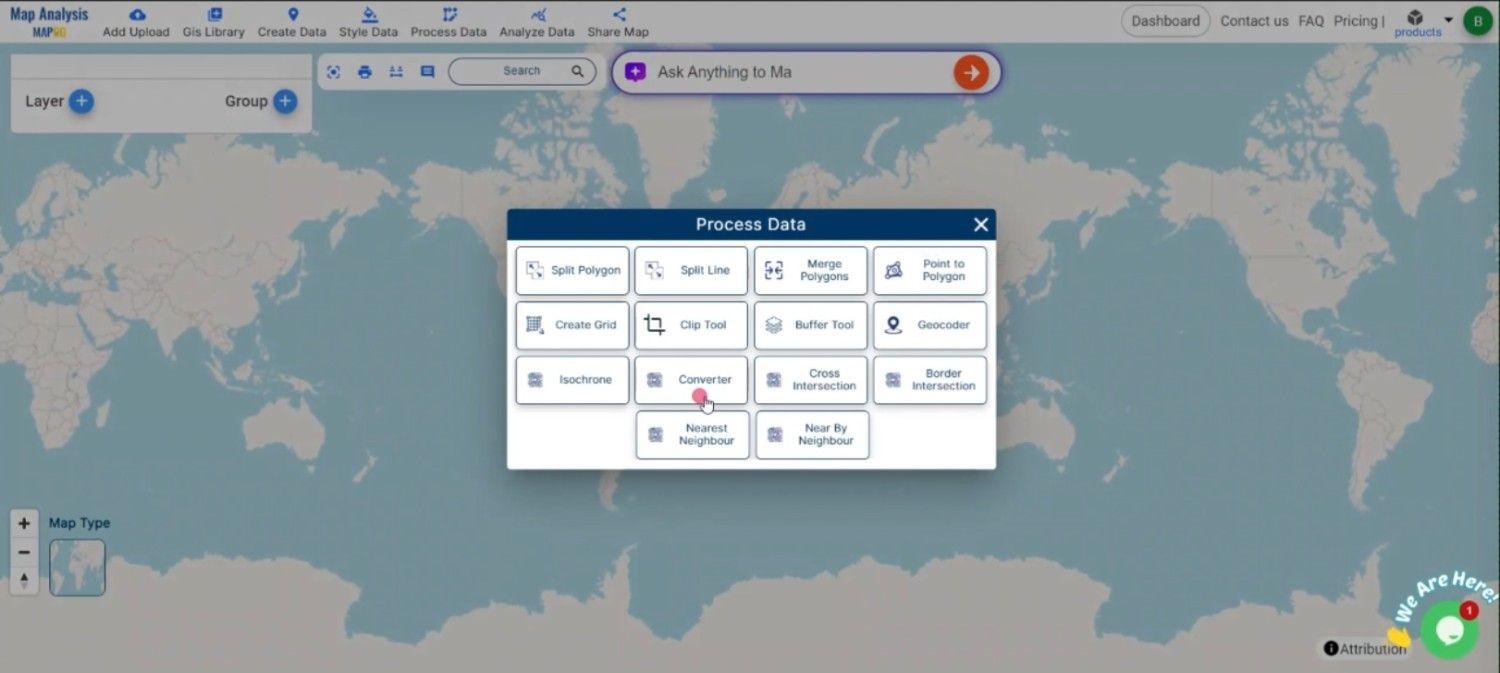
Start by navigating to the “Process Data” section in MAPOG MapAnalysis. Select the “Converter Tool” option. Before uploading your SHP file, ensure it is organized and ready for conversion.
Step 2: Select the Format for Conversion
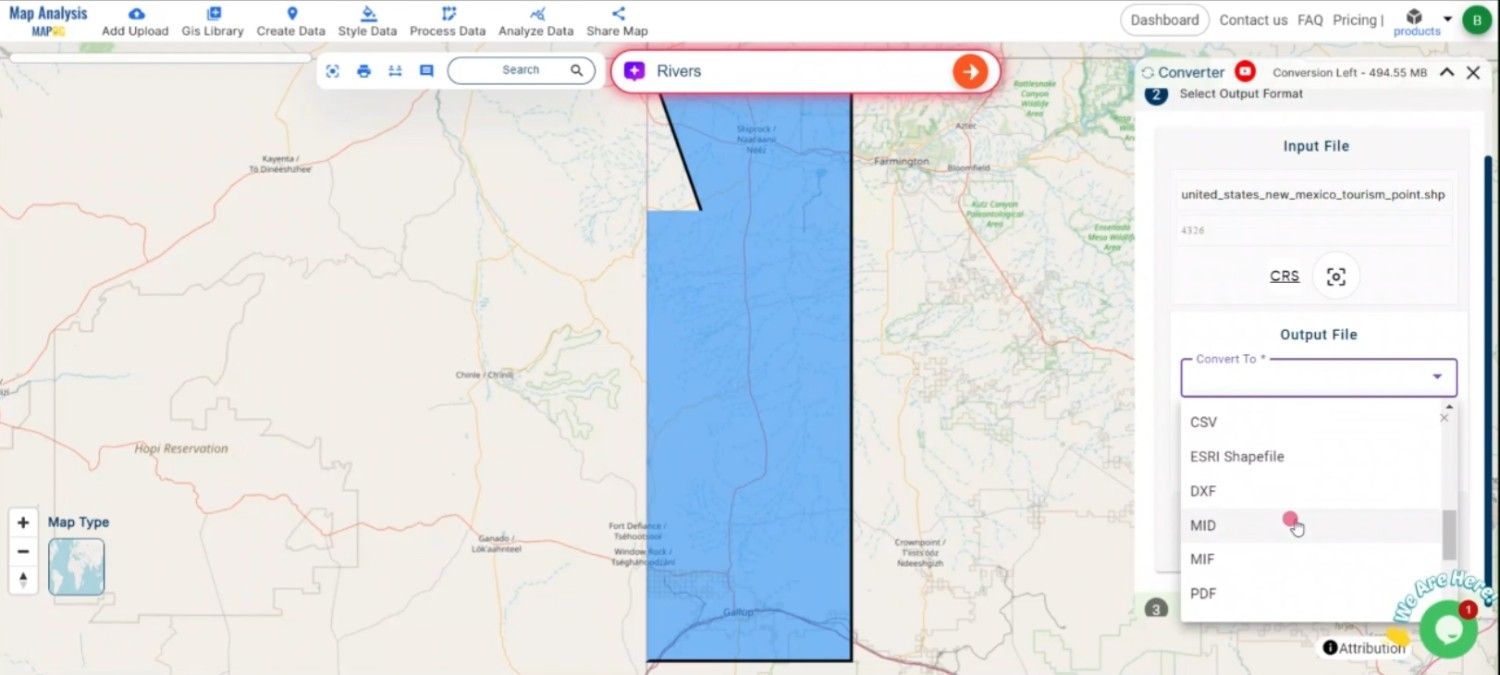
Next, choose MID as the output format. MID is ideal for storing attribute data associated with geographic features, making it suitable for MapInfo applications.
Step 3: Choose the Output Coordinate Reference System (CRS)
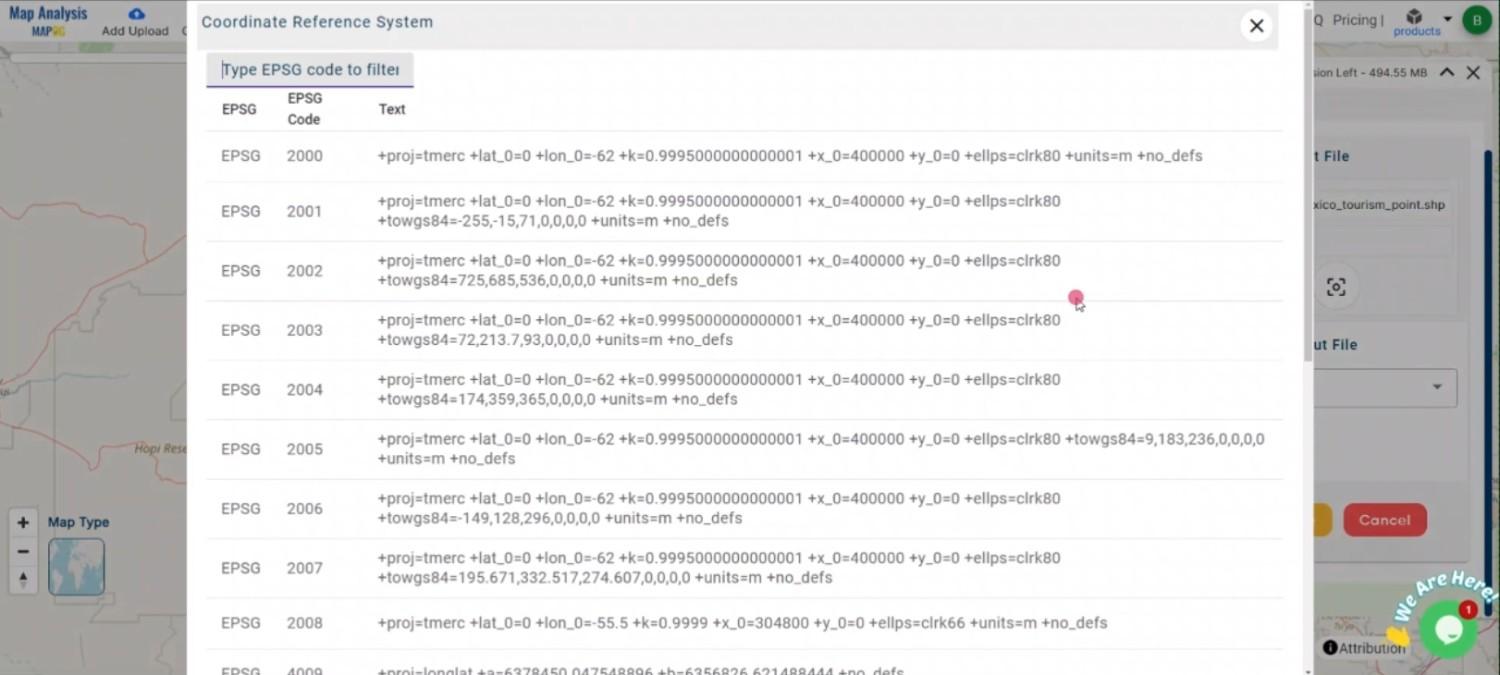
If your data includes spatial information, select the appropriate CRS to ensure accurate geographic positioning in your MID file.
Step 4: Execute the Conversion
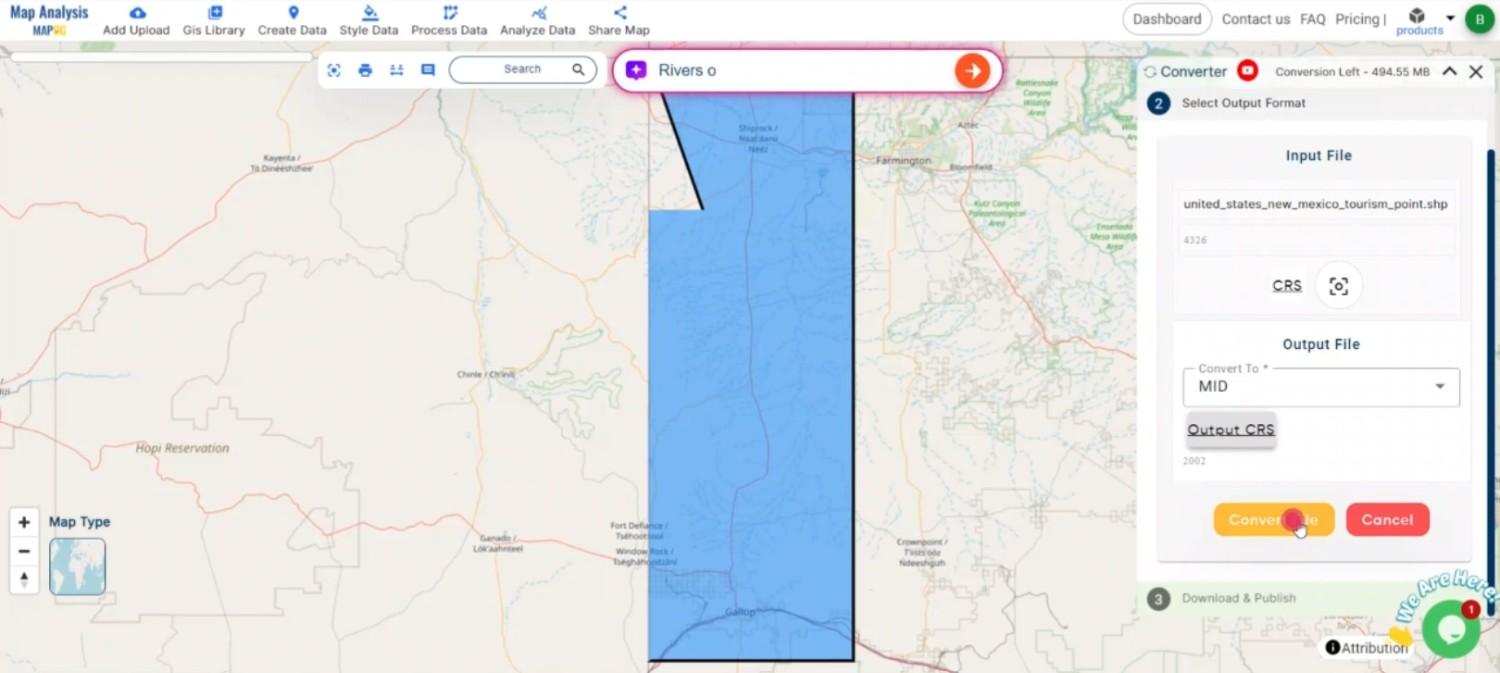
Once you’ve selected the MID format and set the CRS, initiate the conversion process. The MAPOG tool will accurately convert your SHP file into MID format, ensuring that both geographic and attribute data are preserved.
Step 5: Review and Download
After the conversion is complete, review the output to confirm the data was correctly converted. Finally, download the MID file, which is now ready to be used within MapInfo GIS applications.
Conclusion:
The MAPOG Converter Tool simplifies the process of converting GIS data between different formats, making it an essential resource for GIS professionals. By following these steps, you can easily convert SHP files to MID format, ensuring your spatial and attribute data are well-prepared for use in MapInfo systems. If you need to download any data file in SHP or in any other formats like GML, TOPOJSON. Visit GIS DATA, here we have 900+ data layers for 200+ countries.
Feature Tool:
- Nearest Neighbour
- Spatial Join
- Quantity Style
- Create Point Data
Story by MAPOG:
For those who wish to create lively and attractive maps that graphically involve MAPOG is ideal. By utilizing maps with multimedia elements like text and photographs, it helps you to create amazing tales. Making shared material is simple with Story by MAPOG, whether you’re taking a tour, presenting research, or promoting a project.
Here are some other blogs you might be interested in:
- Convert Online Gis data : KML to PDF file
- Converting KML to GeoTIFF , Online Gis Data Converter
- Converting KMZ to SHP : Online GIS Data Conversion
- Converting TopoJSON to SHP Online : GIS Data Converter
- Converting GeoJSON to CSV with MAPOG
- Converting GML to KML with MAPOG
- Convert KMZ to TopoJSON Online
- Converting KMZ to GeoJSON Online
- Convert KML to MID Online
- Online Conversion KML to MIF
- Convert KML to GPKG Online
- Convert GML to SHP Online
- Convert KML to GML Online
- Convert KML to GeoJSON file online
- Convert KML to TopoJSON Online
- SHP to GPX / GPS
- Convert GeoJSON to KML
- Convert Geojson to MIF MapInfo file
- GeoJSON to Shapefile
- Convert KMZ to GPX