With the advancements in today’s digital world, GIS data is a necessary element for any professional or enthusiast in urban planning, environmental monitoring, or simply the creation of a visual story. The integration of GIS data with an online map is, thus, an indispensable skill. In the following pages, we shall describe how to incorporate GIS data with an online map using MAPOG‘s interactive interface.
Why Use GIS Data on Online Maps?
GIS data allows you to visualize and analyze spatial relationships, offering insights that static maps simply can’t provide. MAPOG empower users to:
- Integrate layers of data for richer context.
- Share interactive maps with ease.
- Create engaging visual stories for various audiences.
Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced user, adding GIS data to an online map can enhance your projects significantly.
Steps to Add GIS Data to an Online Map with MAPOG
1. Access MAPOG’s Mapping Platform
Navigate to the MAPOG platform. The platform’s user-friendly interface allows you to:
- Click on “Create New” in the top-right corner of the homepage. Give your map a meaningful name and a brief description to define its purpose.
- Choose from various base maps, such as satellite views or street maps.
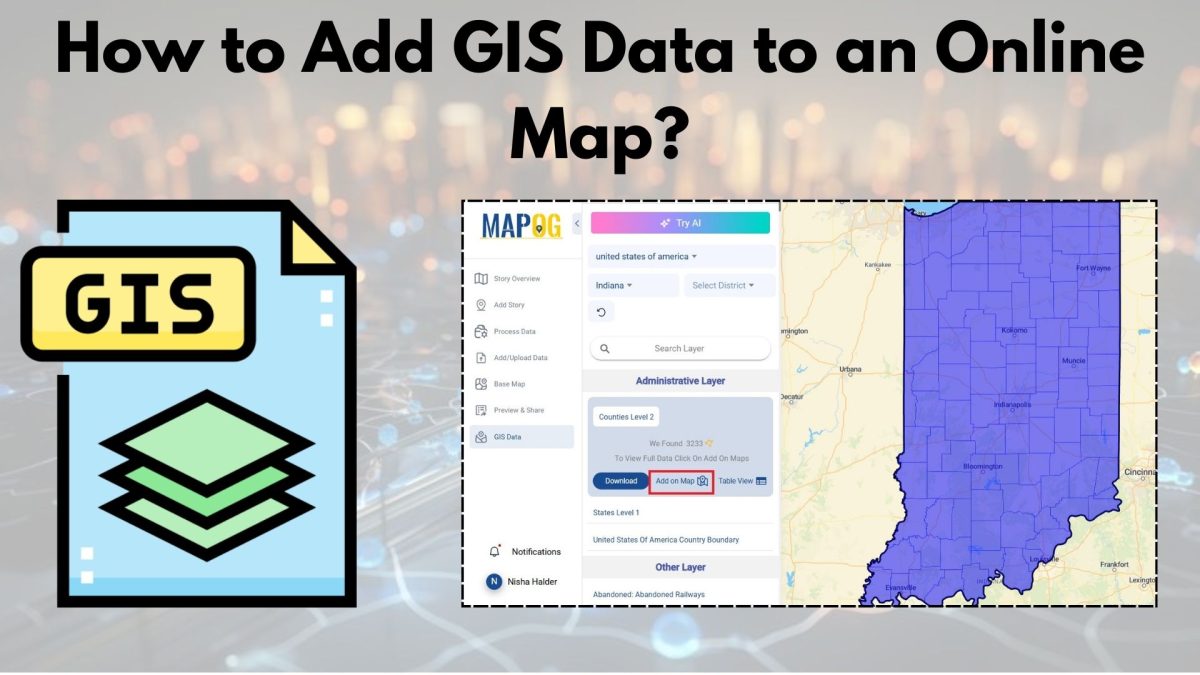
2. Upload GIS Data
- After coming to the interface, On the left panel, select “ Add/Upload Data “. There you’ll get 4 options.
- Easily upload GIS files like SHP, GeoJSON, and more with the “upload vector files” option.
- Import structured datasets like CSV or XLSX with “Upload CSV/Excel File”.
- Include previously used data layers using “Add Existing Layer”.
- Explore layers covering 2,000+ fields—agriculture, transportation, rivers, and more with “GIS data”.
Ensure your data aligns with the intended layers to avoid overlaps.
3. Customize Map Features
After importing your data, enhance its usability by:
- Add on Map: With the “Add on Map” option, overlay your desired data onto your map. You can integrate it into the existing map for advanced spatial analysis.
2. Utilize Feature Tools: Utilize various kinds of tools for your spatial analysis to shape your work properly. You can style your data in different ways to visualize properties and attributes, you can effortlessly perform polyline splitting, use the Converter Tool for various formats, calculate isochrones, and utilize the Export Tool.
4. Test and Publish Your Map
Once satisfied with your map:
- Preview it to ensure accuracy.
- Share it as a public link or embed it in your website.
Interactive maps can also be integrated into reports or presentations, providing dynamic visuals for stakeholders.
Tips for Effective GIS Mapping
- Keep It Simple: Avoid clutter by focusing on key data points.
- Leverage Interactivity: Use clickable features to display additional information.
- Optimize for Mobile: Ensure your map is responsive for users on different devices.
For instance, when mapping a city’s transportation network, include clickable routes that display schedules and stops.
Examples of GIS Applications
- Urban Planning: Overlay zoning maps with population data to identify areas for development.
- Environmental Monitoring: Track deforestation or water quality changes over time.
- Tourism: Highlight popular attractions with details on accessibility and visitor tips.
These use cases demonstrate the versatility of GIS data in creating impactful maps.
Conclusion
Adding GIS data to an online map is relatively easy with the right tools. MAPOG can make complex data easier to understand and share it with a wider audience. Start experimenting with GIS data today and see how interactive maps can transform your projects.
Have you tried creating a map with GIS data? Share your experiences and tips in the comments below!
Here are some other blogs you might be interested in
- Protecting Wetlands: Guide to Create GIS Map for Nature
- Mapping Tiger Attack Hotspots – Create an Online Map and Share
- Make Routes for Military Aerial Planning- Through Bearing angle and Distance calculation – Online Route Compass
- Mapping Healthcare Efficiency: GIS Buffer Analysis of Hospital Locations
- Add WMS- Two step online view of WMS layer on a map
- Plot ATM locations on a map and embed on your website
- Map habitat locations of endangered animals & keep track of their living