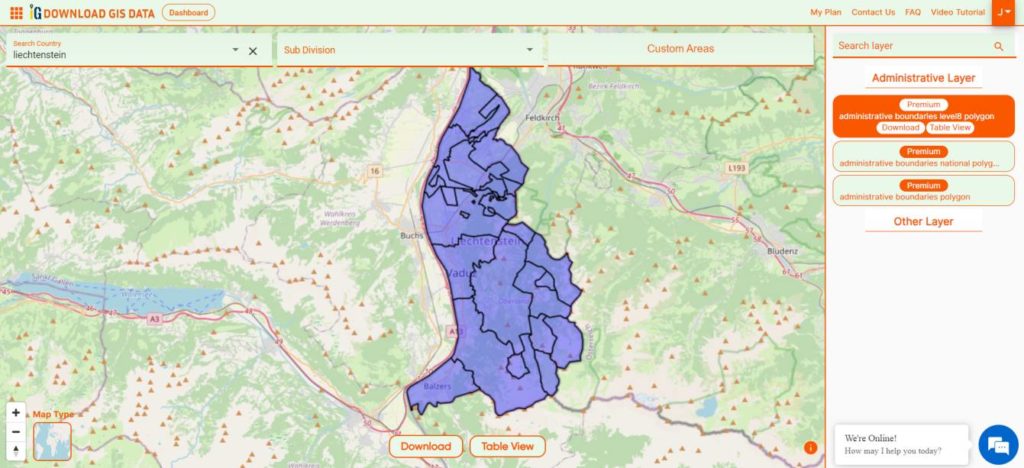
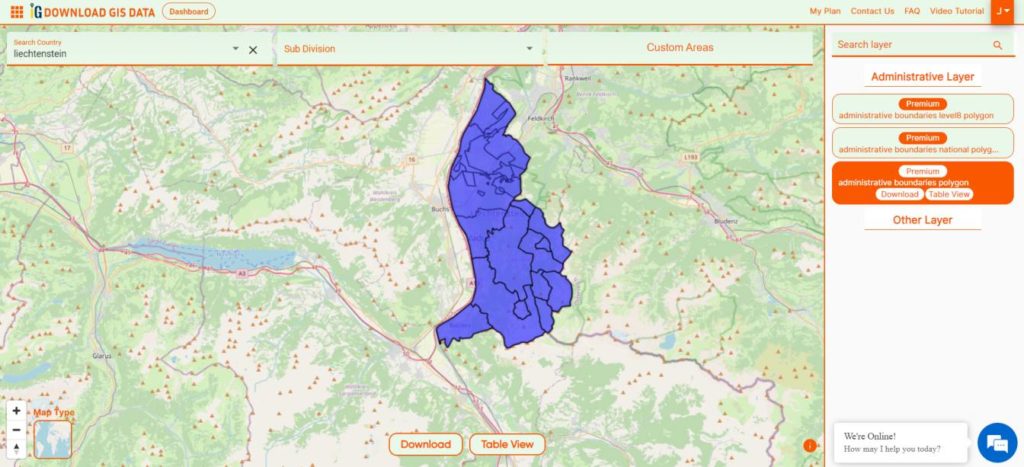
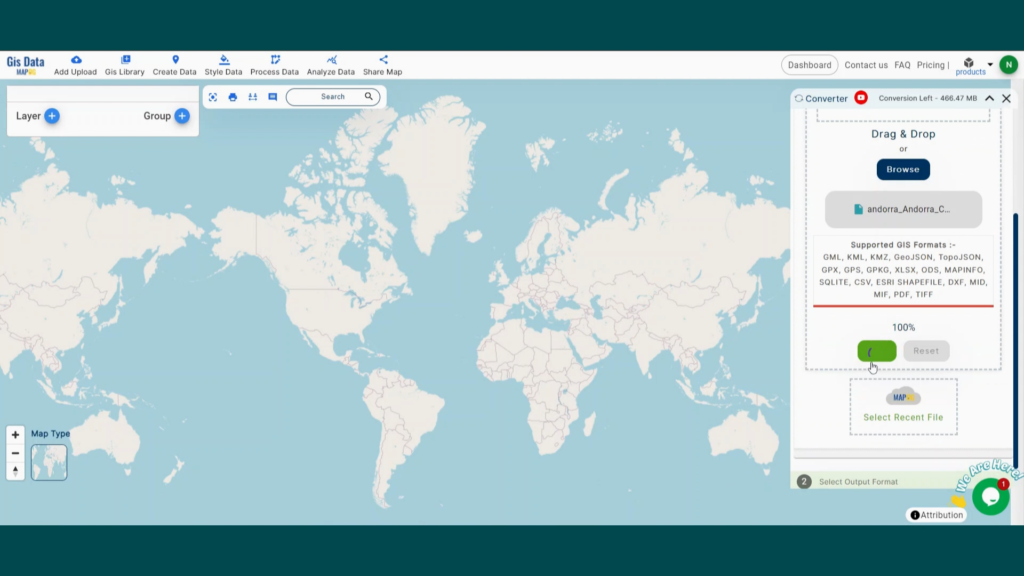
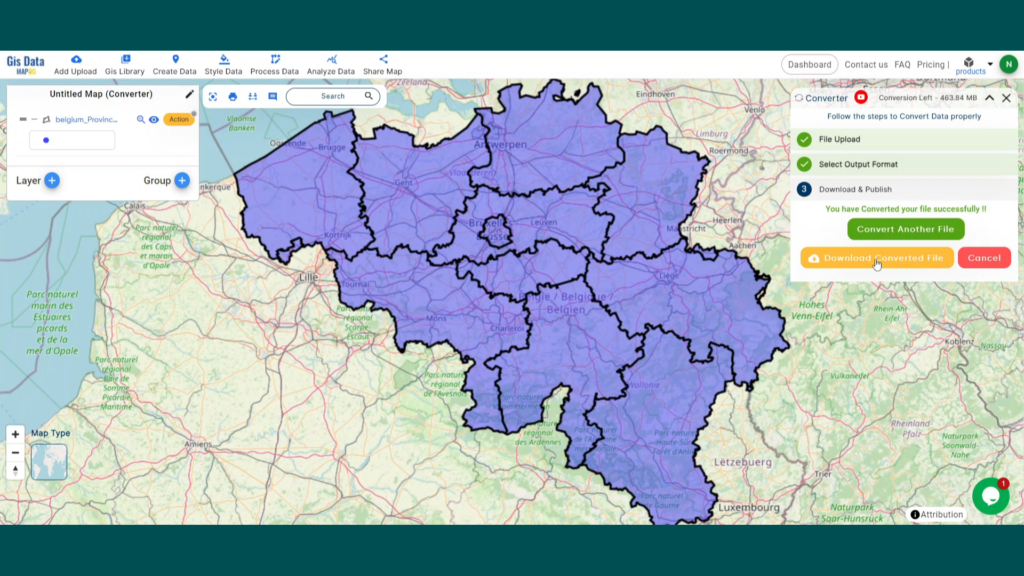
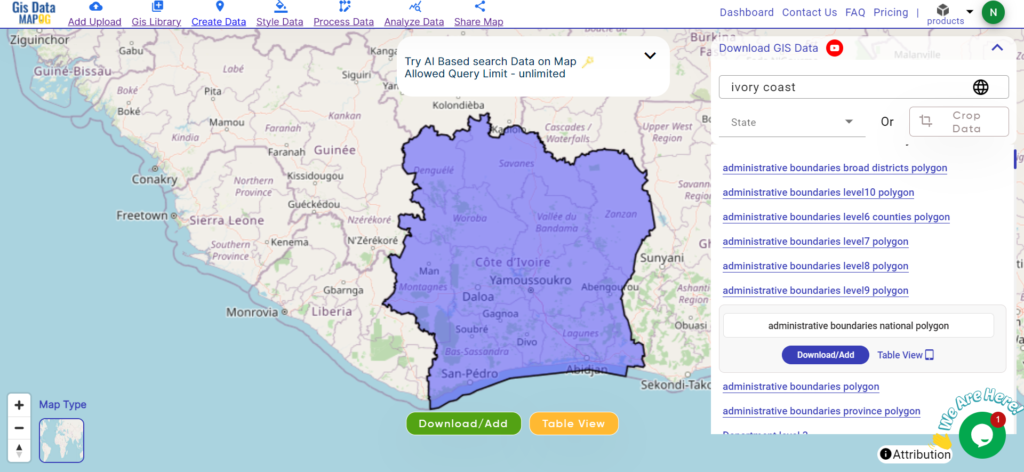
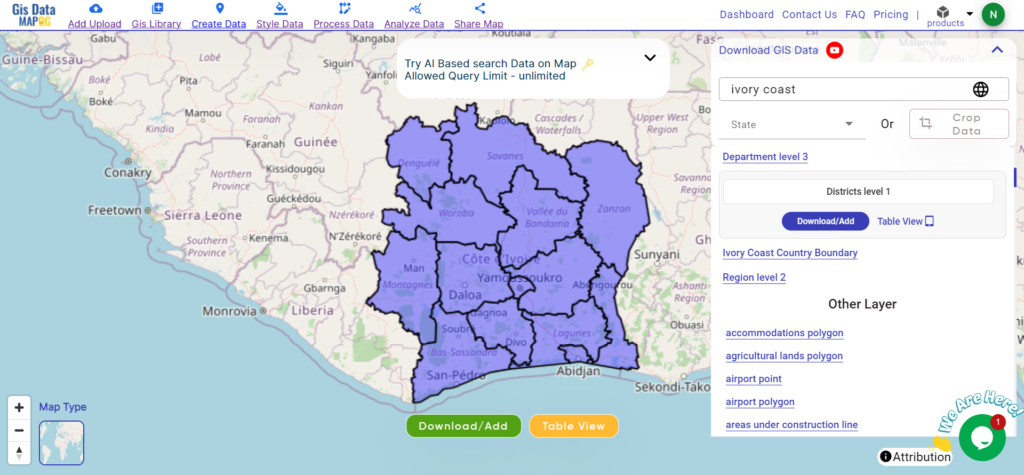
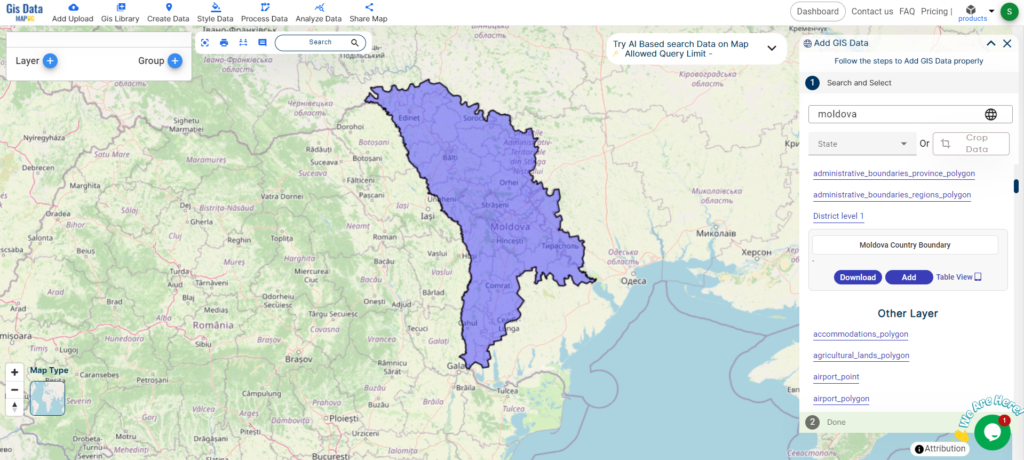
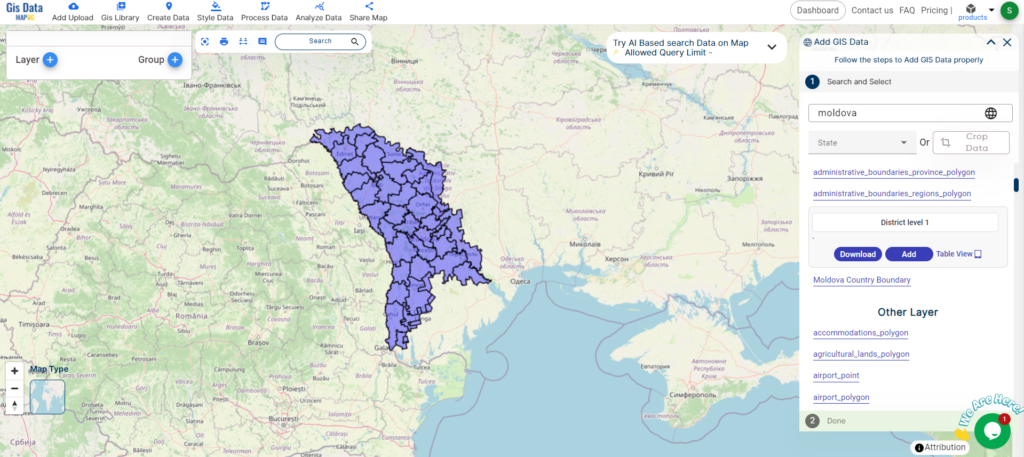
Are you struggling to find accurate and up-to-date GIS data for your desired country? Worry no more, as MAPOG is here to be your ultimate solution! Our platform offers a comprehensive collection of GIS data covering more than 150 countries. You’ll find an impressive selection of over 150 GIS datasets available for each nation in the MAPOG GIS Data Collection. The hallmark of our GIS data lies in its exceptional accuracy, especially when representing administrative divisions. Moreover, our users can access a diverse range of data pertaining to natural and man-made geographic features, including rivers, roads, railway lines, airport locations, and much more, all meticulously represented in appropriate geometric structures (points, lines, and polygons). Facilitating seamless access to this invaluable data are two essential tools – Download GIS Data and Add GIS Data, thoughtfully integrated into the MAPOG platform. To delve deeper into the functionalities of the Add GIS Data tool, check out our enlightening article – “Add GIS data from IGISMap GIS data collection“
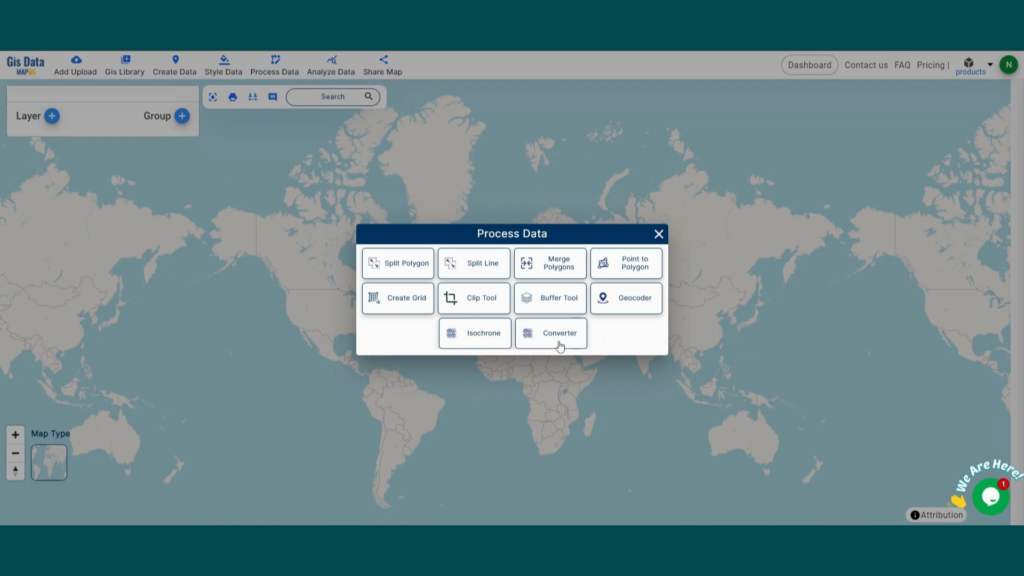
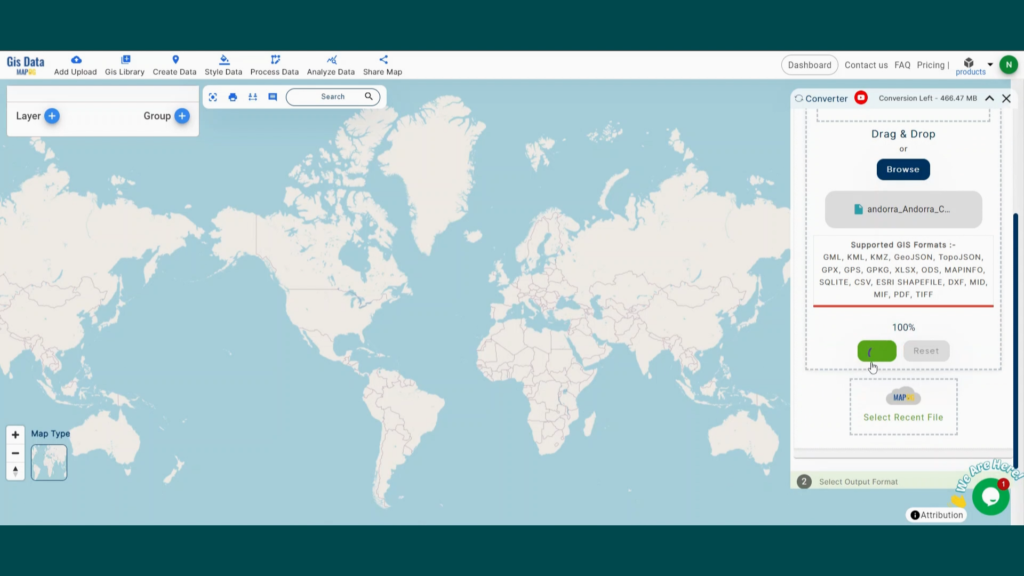
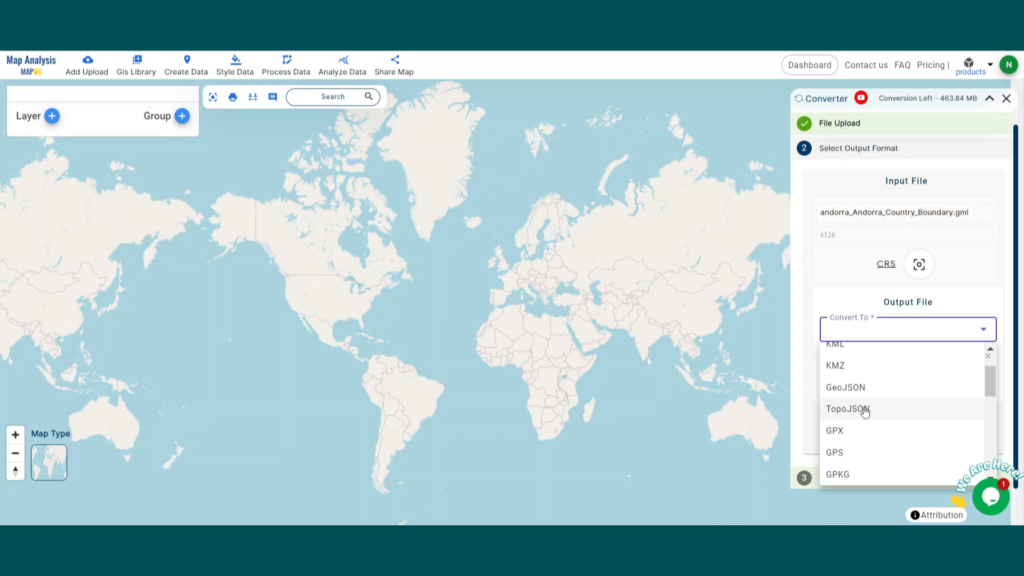
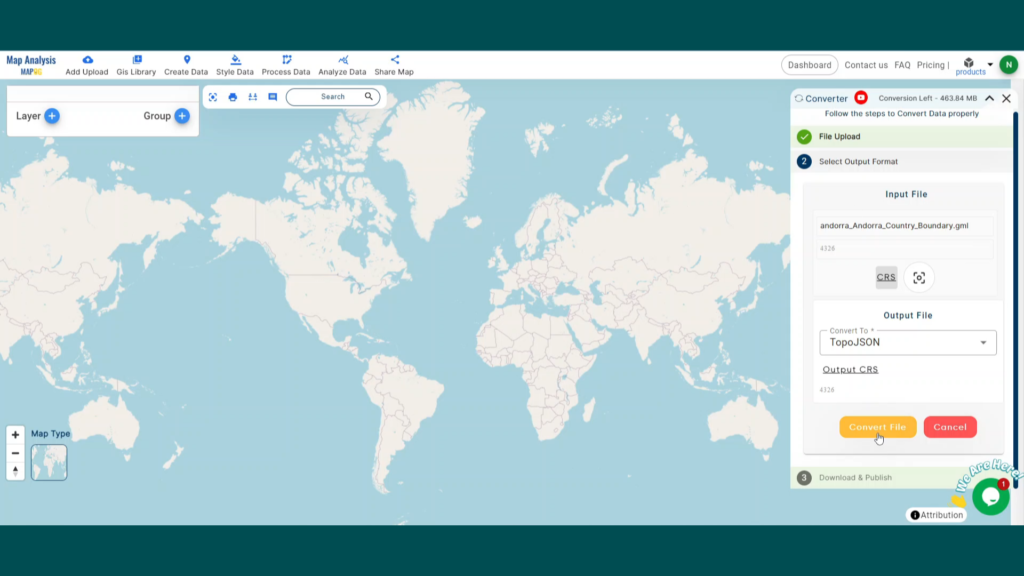
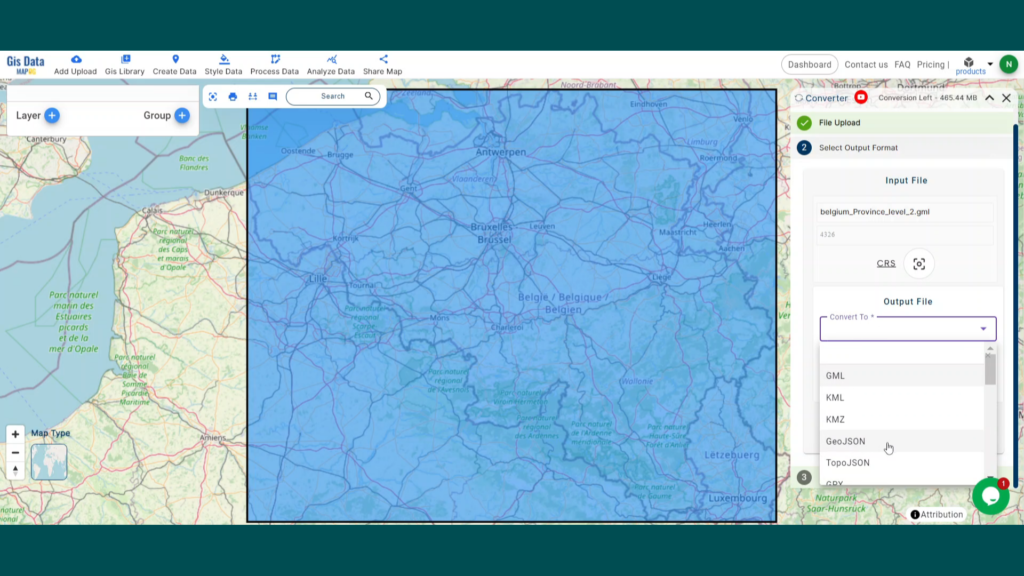
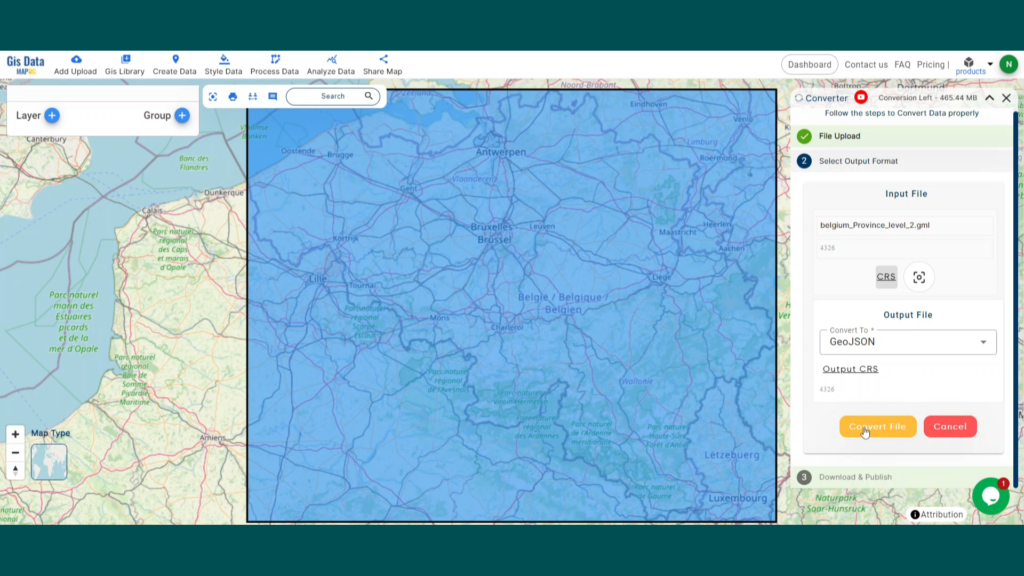
With MAPOG’s versatile toolkit, you can effortlessly upload vector, add WMS (Web Map Service) layers, upload Excel or CSV data, incorporate existing files, perform polygon splitting and merging, generate new polygon and polyline data, use the converter for various formats, conduct buffer analysis, create grids, transform points into polygons, calculate isochrones, and utilize the geocoder for precise location information.
We offer an extensive array of data formats, including KML, SHP, CSV, GeoJSON, Tab, SQL, Tiff, GML, KMZ, GPKZ, SQLITE, Dxf, MIF, TOPOJSON, XLSX, GPX, ODS, MID, and GPS, ensuring compatibility and accessibility for various applications and analyses.
Note:
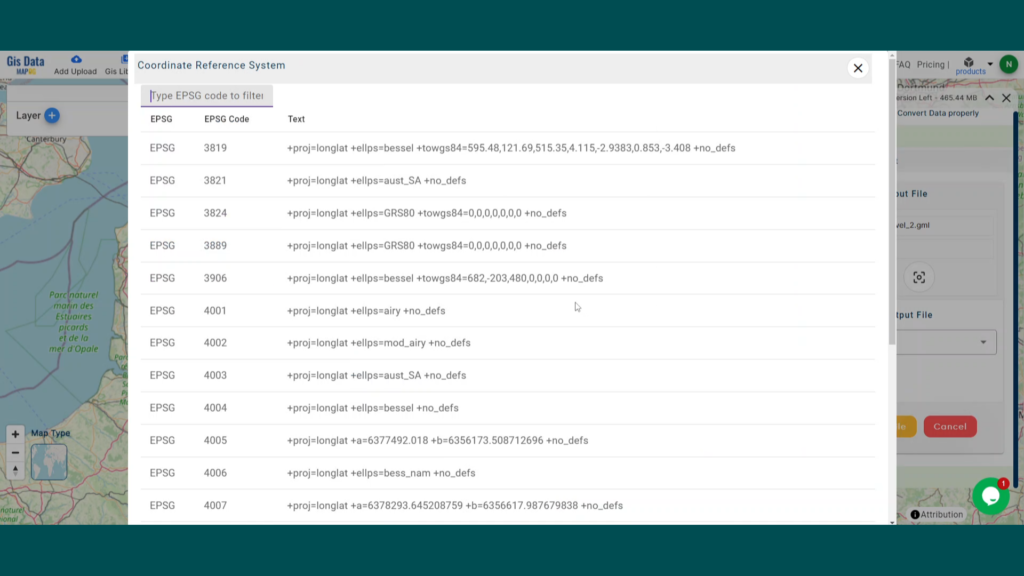
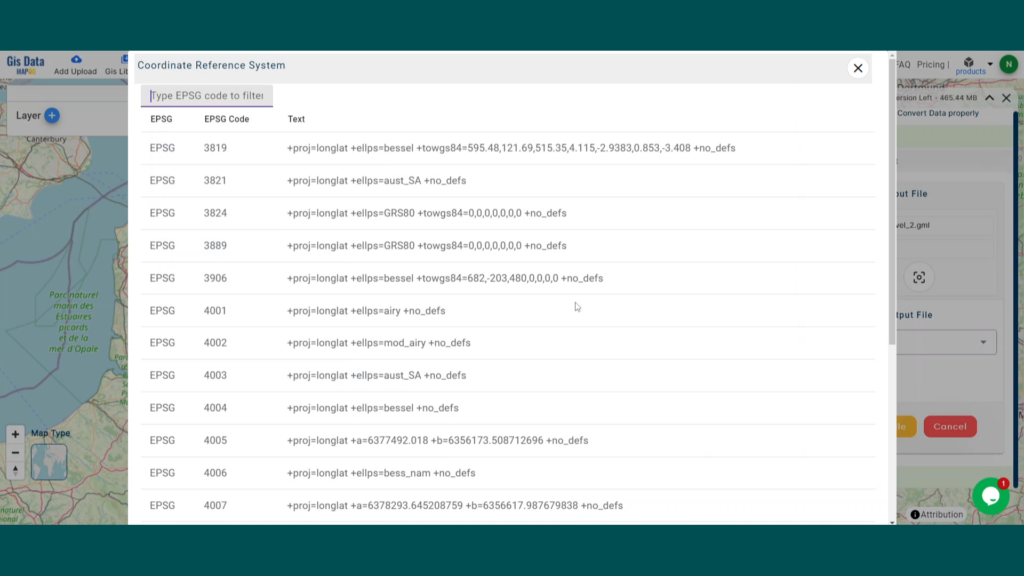
- All data available are in GCS datum EPSG:4326 WGS84 CRS (Coordinate Reference System).
- You need to login for downloading the shapefile.
Download Shapefile Data of Cape Verde
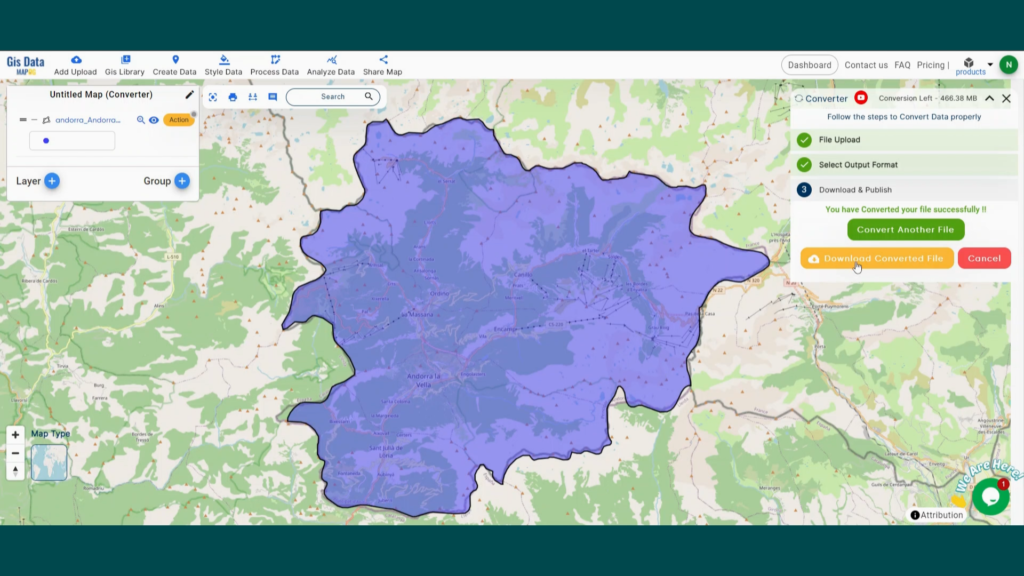
The Cape Verde archipelago is in the Atlantic Ocean, approximately 570 kilometers (350 mi) off the western coast of the African continent, near Senegal, The Gambia, and Mauritania as well as part of the Macaronesia ecoregion. It lies between latitudes 14° and 18°N, and longitudes 22° and 26°W. The country is a horseshoe-shaped cluster of ten islands (nine inhabited) and eight islets, that constitute an area of 4033 km2 (1557 sq mi).
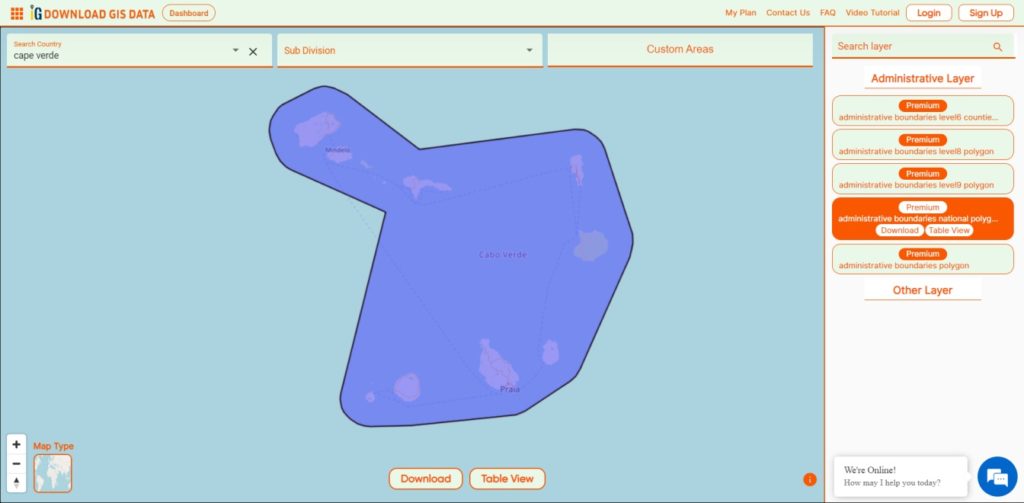
Download Cape Verde National Boundary Shapefile
Download Cape Verde Municipalities Shapefile Data
Cape Verde is divided into 22 concelhos municipalities.
- Tarrafal
- São Miguel
- São Salvador do Mundo
- Santa Cruz
- São Domingos
- Praia
- Ribeira Grande de Santiago
- São Lourenço dos Órgãos
- Santa Catarina
- Brava
- São Filipe
- Santa Catarina do Fogo
- Mosteiros
- Maio
- Boa Vista
- Sal
- Ribeira Brava
- Tarrafal de São Nicolau
- São Vicente
- Porto Novo
- Ribeira Grande
- Paul
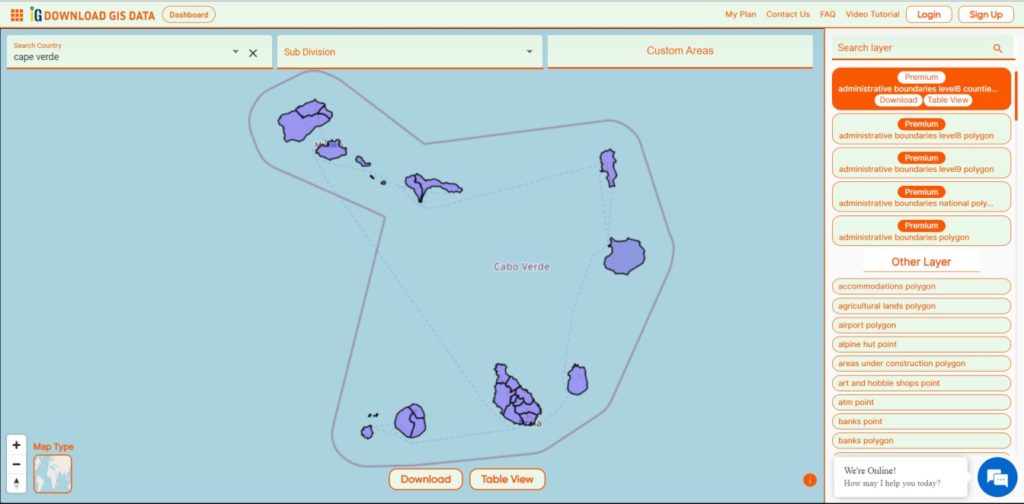
Download Cape Verde Municipalities Boundaries Shapefile
Other GIS Data:
- Download Cape Verde Highway Lines Shapefile
- Download Cape Verde ATM Point Shapefile
- Download Cape Verde Ferry Terminal Point Shapefile
Download Shapefile for the following:
- World Countries Shapefile
- Australia
- Argentina
- Austria
- Belgium
- Brazil
- Canada
- Denmark
- Fiji
- Finland
- Germany
- Greece
- India
- Indonesia
- Ireland
- Italy
- Japan
- Kenya
- Lebanon
- Madagascar
- Malaysia
- Mexico
- Mongolia
- Netherlands
- New Zealand
- Nigeria
- Papua New Guinea
- Philippines
- Poland
- Russia
- Singapore
- South Africa
- South Korea
- Spain
- Switzerland
- Tunisia
- United Kingdom Shapefile
- United States of America
- Vietnam
- Norway
- Chile
- Crotia
Disclaimer : If you find any shapefile data of country provided is incorrect do contact us or comment below, so that we will correct the same in our system as well we will try to correct the same in OpenStreetMap.