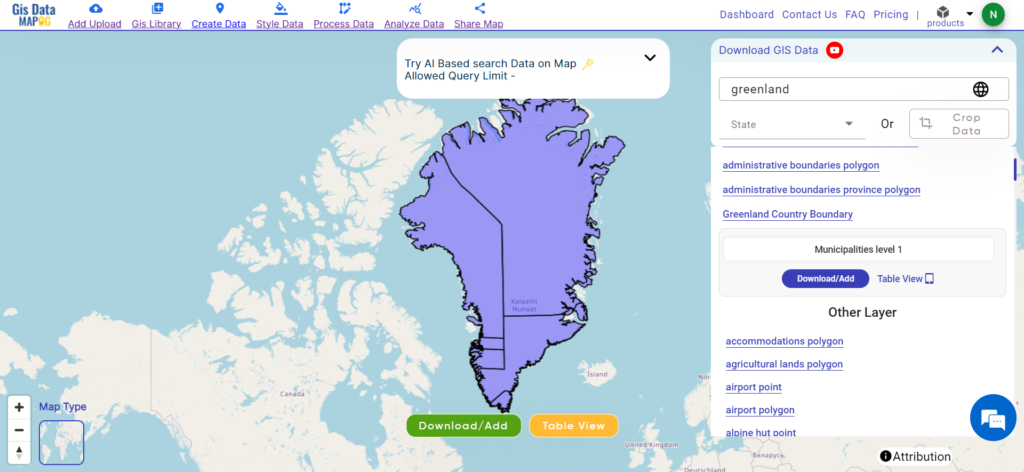
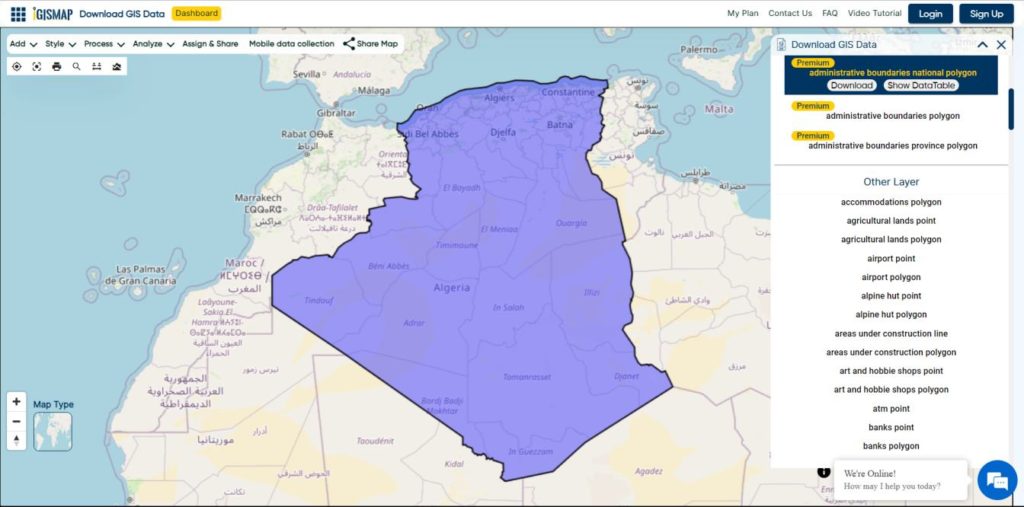
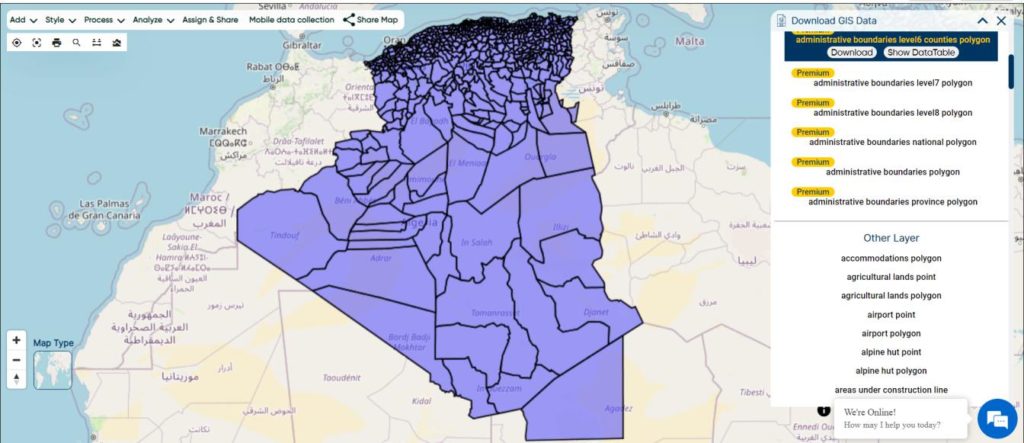
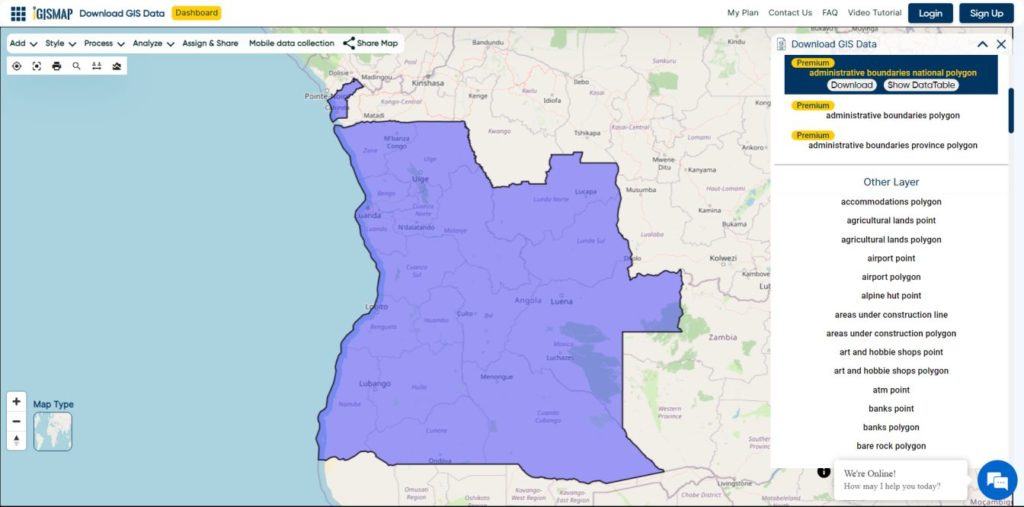
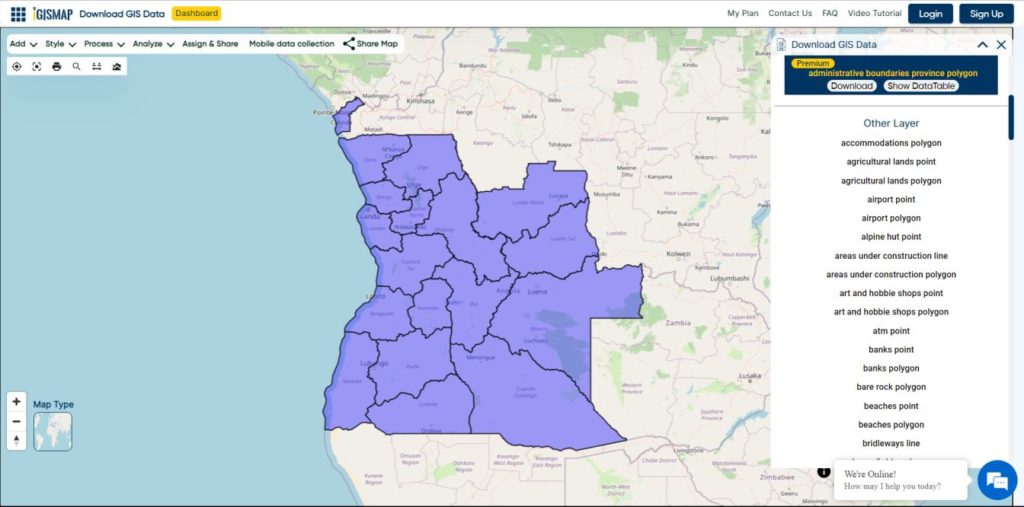
Explore geography of China seamlessly with MAPOG. Access a diverse range of datasets, including boundaries, rivers, vegetation, and airports. Take advantage of user-friendly tools like Download GIS Data, providing formats such as Shapefile, KML, GeoJSON, and CSV. Delve into China GIS Data confidently with MAPOG.
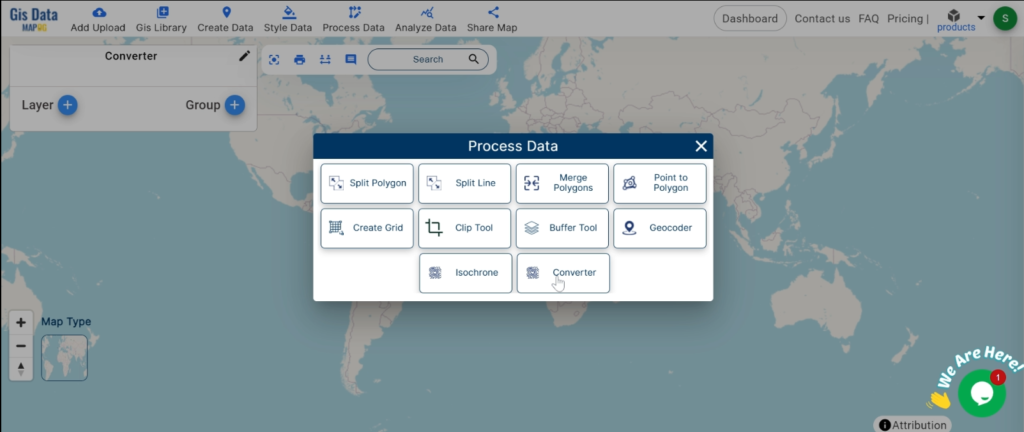
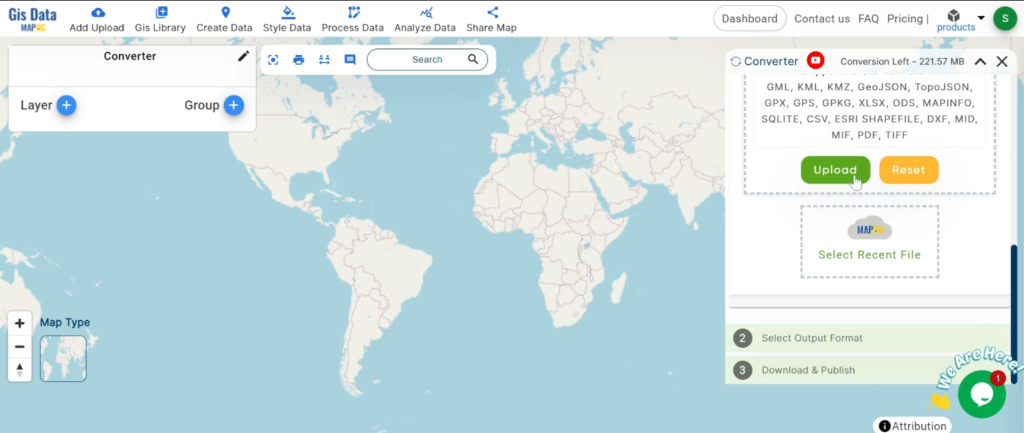
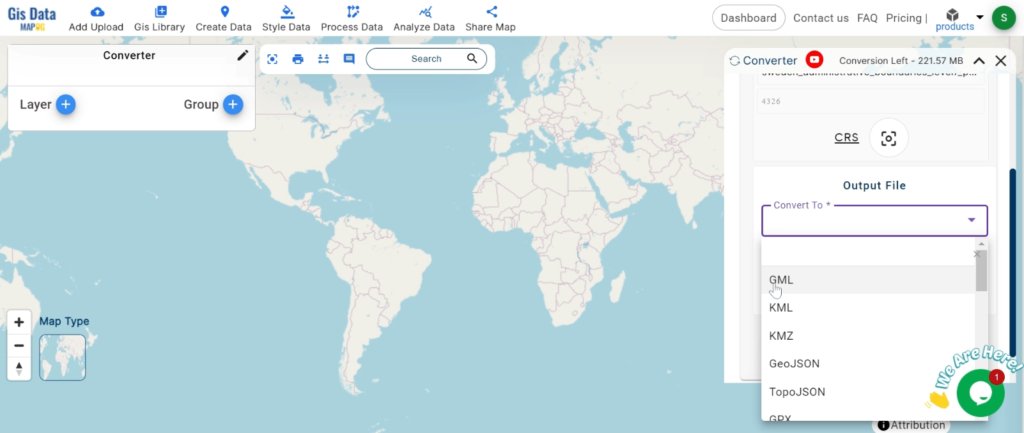
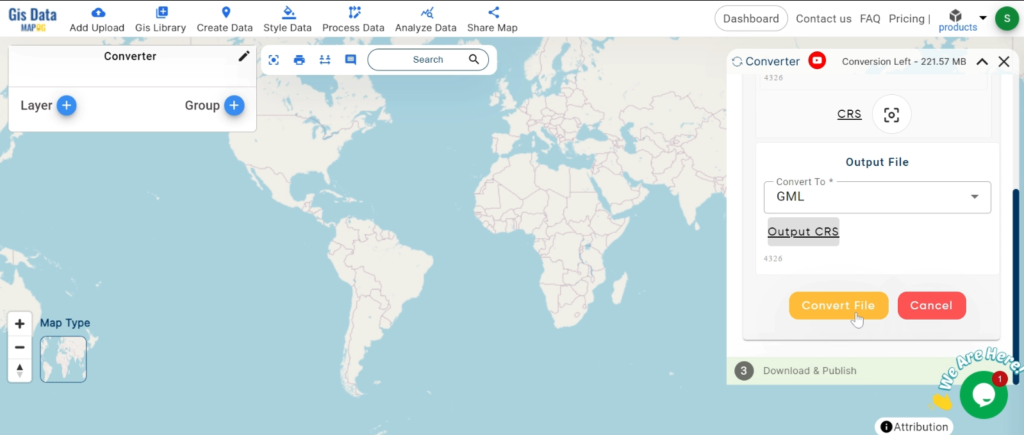
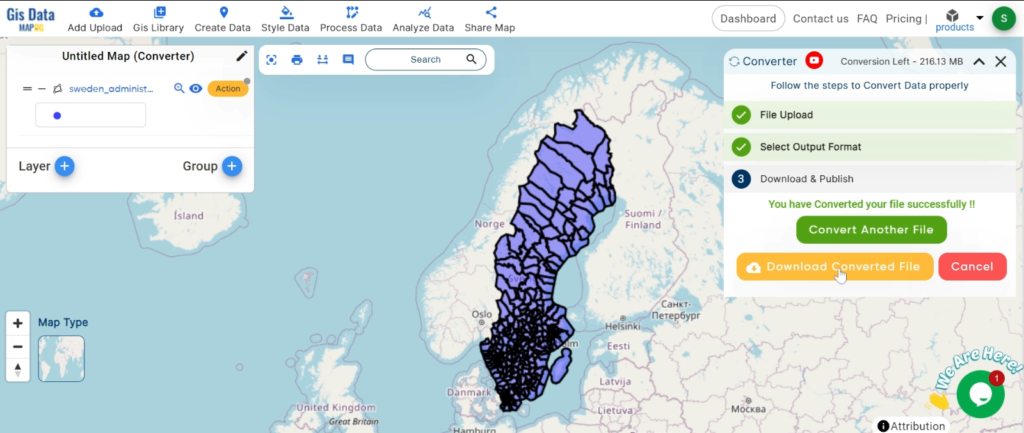
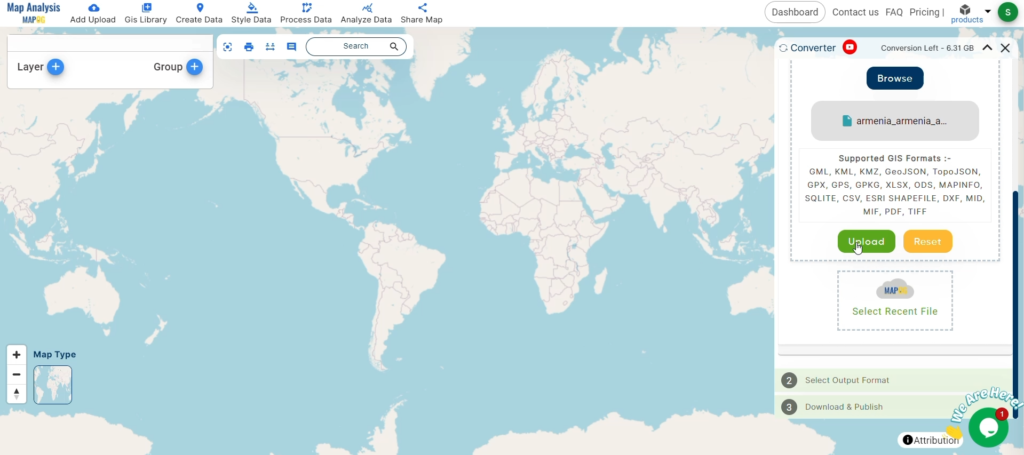
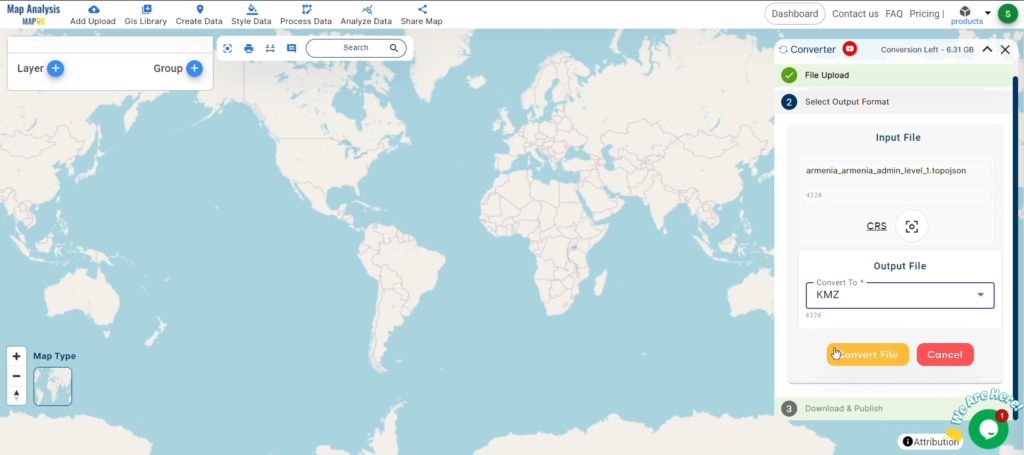
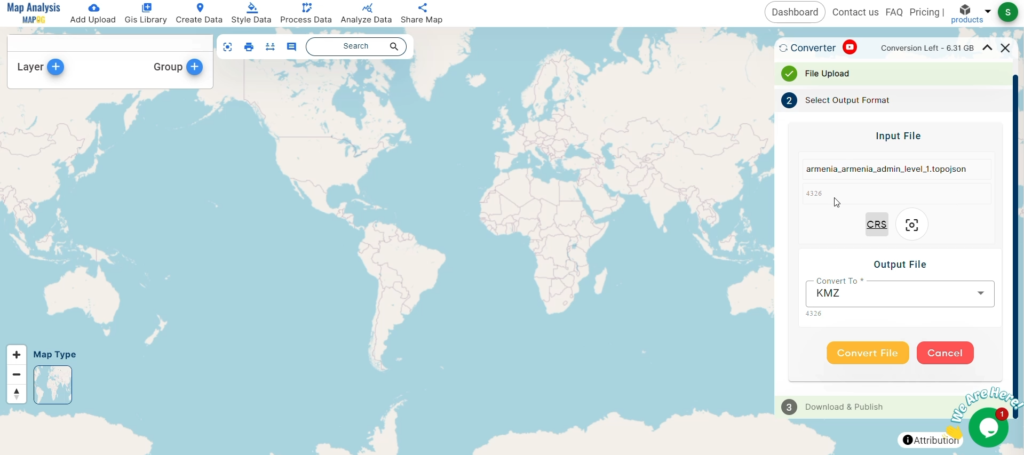
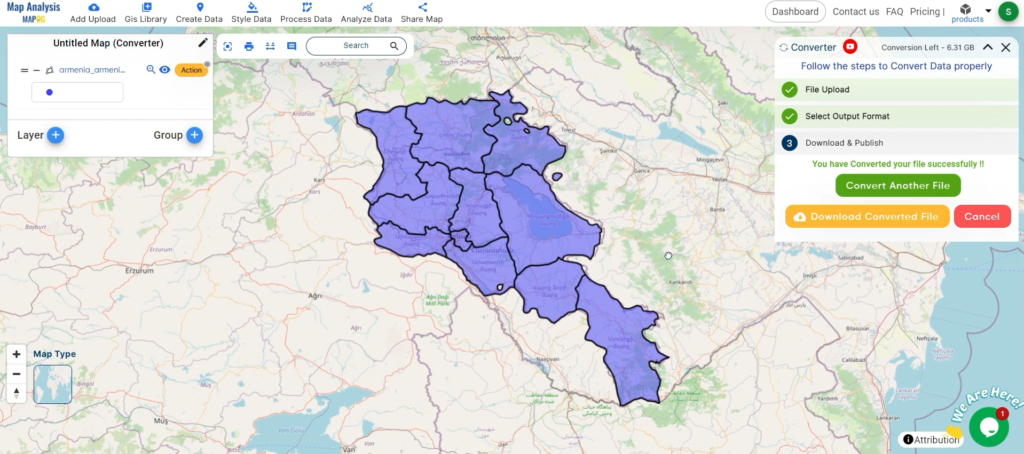
With MAPOG’s versatile toolkit, you can effortlessly upload vector, add WMS (Web Map Service) layers, upload Excel or CSV data, incorporate existing files, perform polygon splitting and merging, generate new polygon and polyline data, use the converter for various formats, conduct buffer analysis, create grids, transform points into polygons, calculate isochrones, and utilize the geocoder for precise location information.
We offer an extensive array of data formats, including KML, SHP, CSV, GeoJSON, Tab, SQL, Tiff, GML, KMZ, GPKZ, SQLITE, Dxf, MIF, TOPOJSON, XLSX, GPX, ODS, MID, and GPS, ensuring compatibility and accessibility for various applications and analyses.
Note:
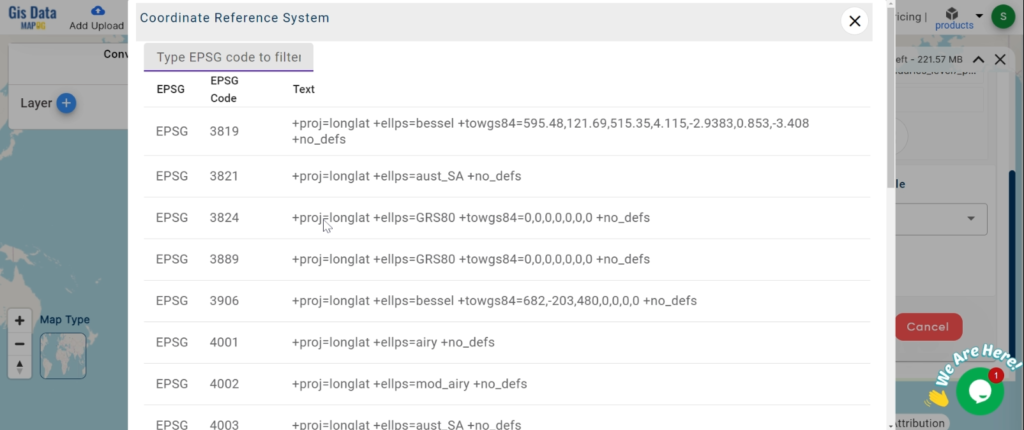
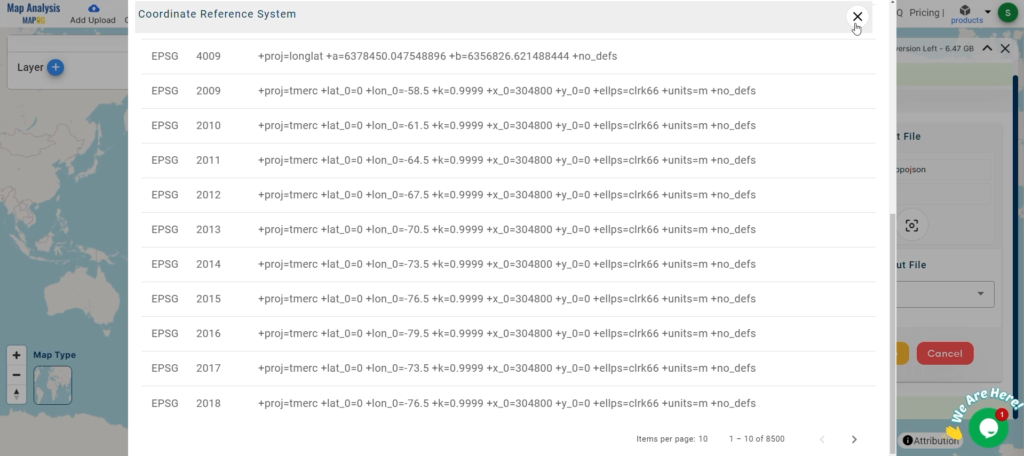
- All data available are in GCS datum EPSG:4326 WGS84 CRS (Coordinate Reference System).
- You need to login for downloading the shapefile.
Download Shapefile Data of Monaco
Monaco, nestled along the French Riviera, is a microstate known for its opulence and glamour. With an area of merely 2.02 square kilometers, it stands as one of the world’s smallest countries. Despite its size, Monaco boasts Monte Carlo as its capital, a bustling city renowned for its lavish casinos, yacht-filled harbors, and prestigious events like the Monaco Grand Prix.
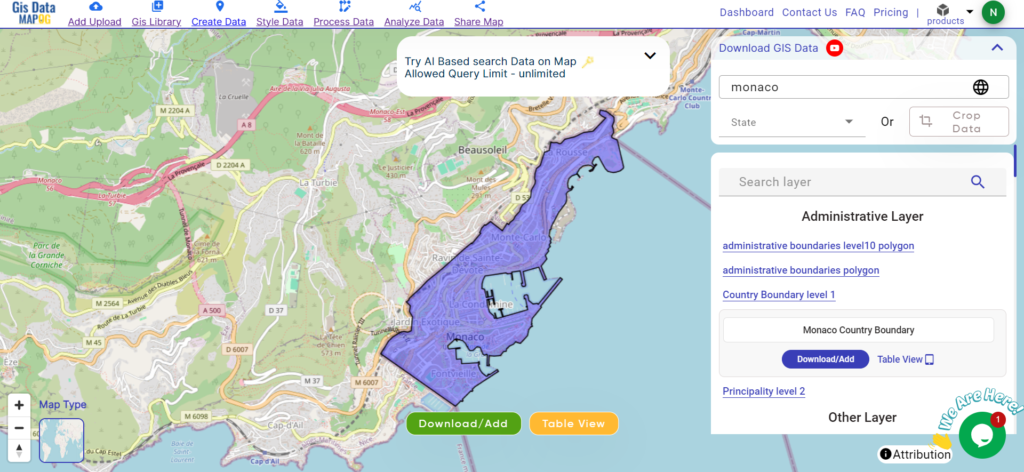
Download Monaco National Boundary Shapefile
Other GIS Data:
- Download Monaco Administrative Boundaries
- Download Monaco ATM Point Shapefile
- Download Monaco bank Point Shapefile
- Download Monaco Road Lines Shapefile
- Download Monaco Bus Point Shape file
Above all links are provided for GIS data of China if you are looking for any specific data, please write us on support@mapog.com
Download Shapefile for the following:
- World Countries Shapefile
- Australia
- Argentina
- Austria
- Belgium
- Brazil
- Canada
- Denmark
- Fiji
- Finland
- Germany
- Greece
- India
- Indonesia
- Ireland
- Italy
- Japan
- Kenya
- Lebanon
- Madagascar
- Malaysia
- Mexico
- Mongolia
- Netherlands
- New Zealand
- Nigeria
- Papua New Guinea
- Philippines
- Poland
- Russia
- Singapore
- South Africa
- South Korea
- Spain
- Switzerland
- Tunisia
- United Kingdom Shapefile
- United States of America
- Vietnam
- Croatia
- Chile
- Norway
- Maldives
- Bhutan
- Colombia
- Libya
- Comoros
- Hungary
- Laos
- Estonia
- Iraq
- Portugal
- Azerbaijan
- Macedonia
- Romania
- Peru
- Marshall Islands
- Slovenia
- Nauru
- Guatemala
- El Salvador
- Afghanistan
- Cyprus
- Syria
- Slovakia
- Luxembourg
- Jordan
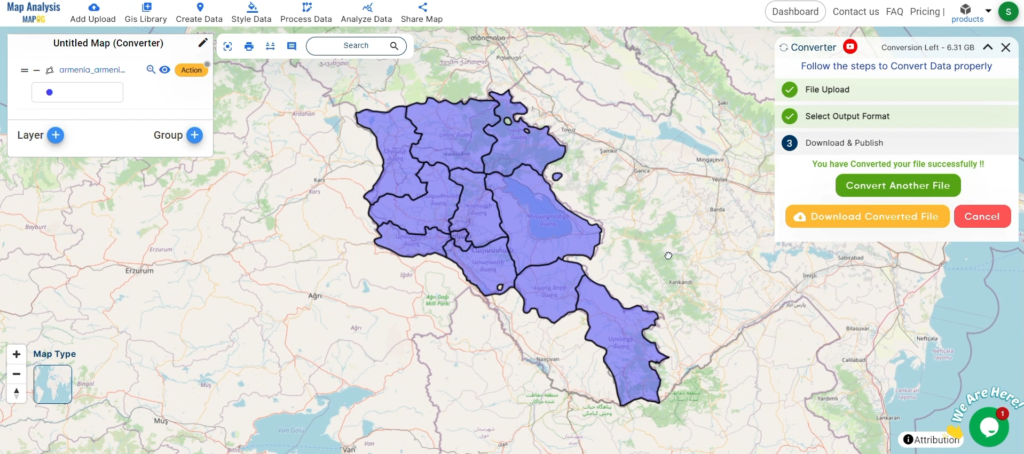
- Armenia
- Haiti And Dominican Republic
- Kiribati
Disclaimer: If you find any shapefile data of country provided is incorrect do contact us or comment below, so that we will correct the same in our system as well we will try to correct the same in OpenStreetMap.