Unlock a world of geospatial insights with MAPOG, your gateway to Download Serbia Administrative Boundary GIS Data. Dive into a treasure trove of datasets covering national, administrative divisions, and more.
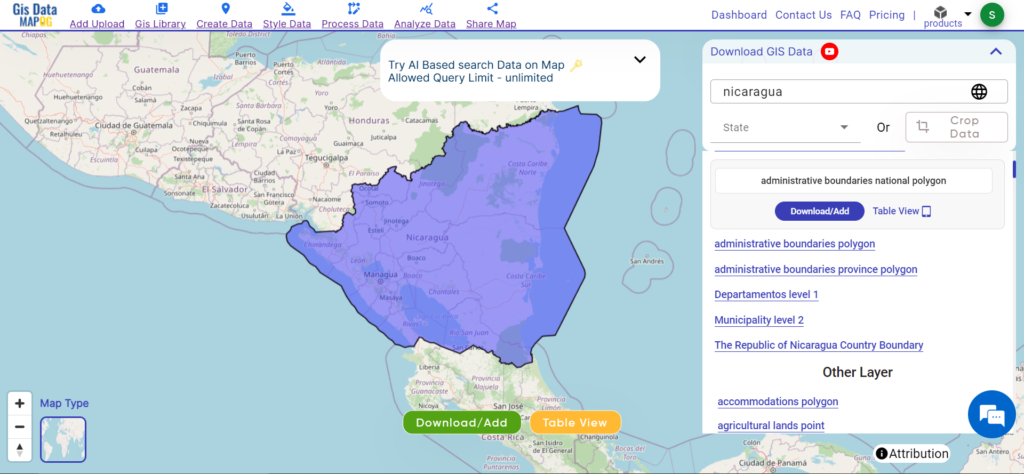
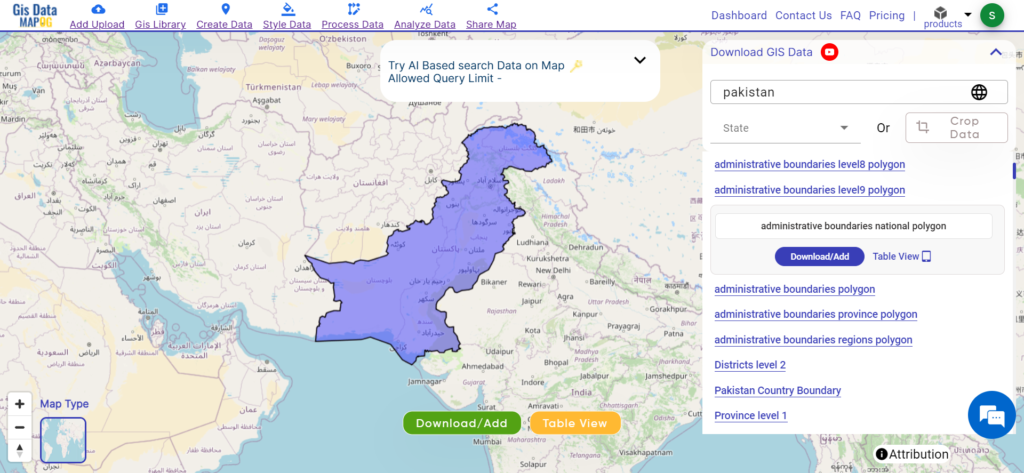
Navigating and Download Serbia Administrative Boundary GIS Data is seamless with MAPOG. Access over 150 meticulously curated datasets detailing administrative boundaries and geographic features such as rivers, roads, and national parks. Our platform offers intuitive tools for effortless exploration: Download GIS Data and Add GIS Data. With the Download GIS Data tool, choose from a variety of formats like Shapefile, KML, GeoJSON, or CSV to obtain the precise data you need. Need guidance on using the Add GIS Data tool? Consult our comprehensive guide for step-by-step instructions. Let MAPOG be your trusted companion on an enriching geospatial journey through Serbia’s diverse landscapes.
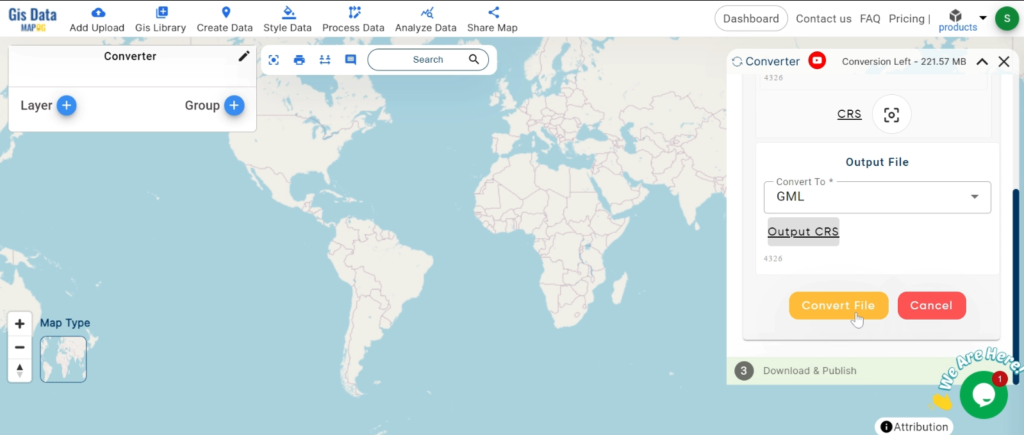
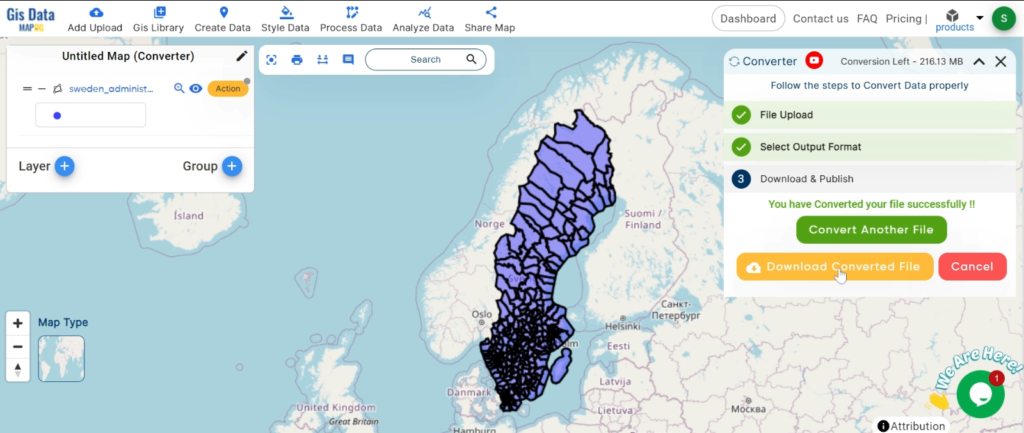
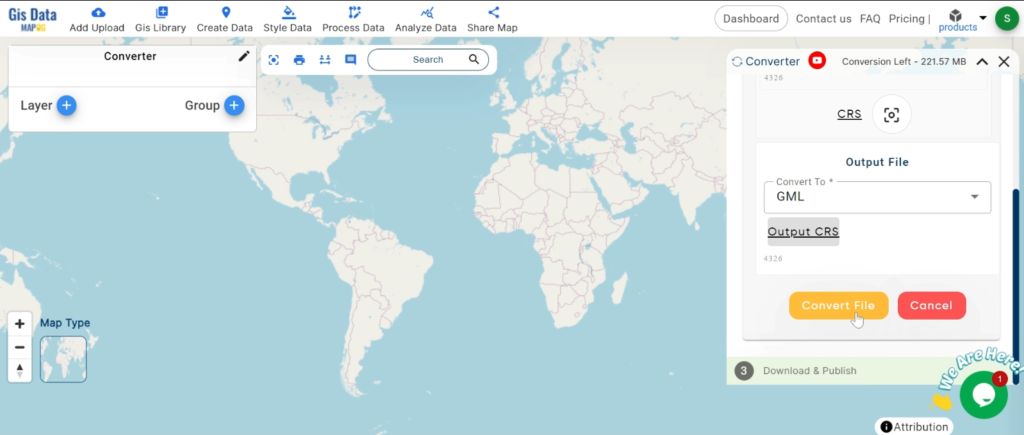
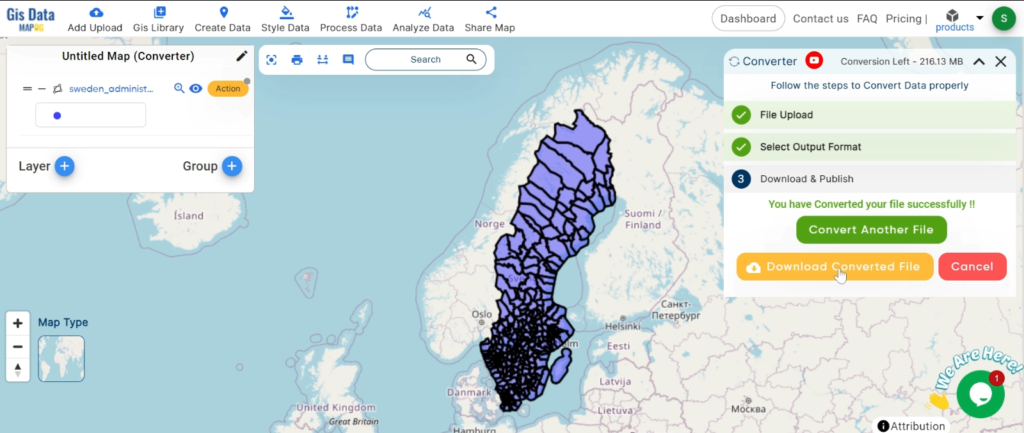
With MAPOG’s versatile toolkit, you can effortlessly upload vector, add WMS (Web Map Service) layers, upload Excel or CSV data, incorporate existing files, perform polygon splitting and merging, generate new polygon and polyline data, use the converter for various formats, conduct buffer analysis, create grids, transform points into polygons, calculate isochrones, and utilize the geocoder for precise location information.
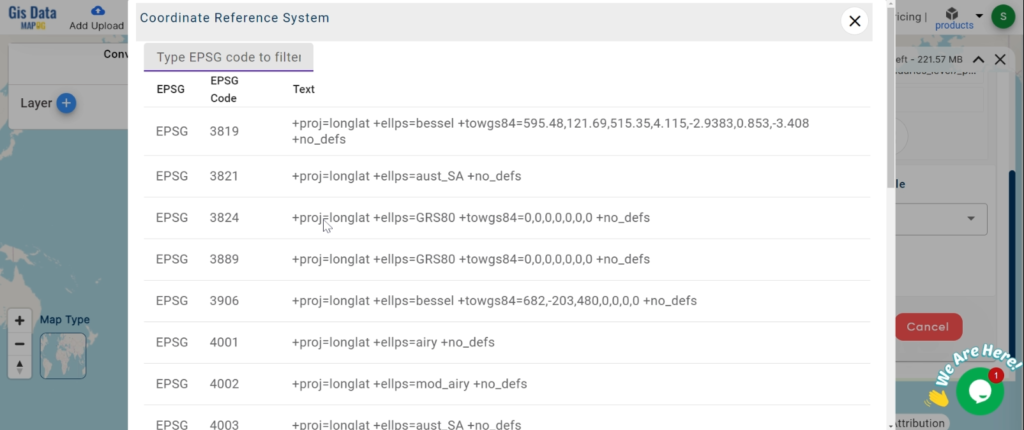
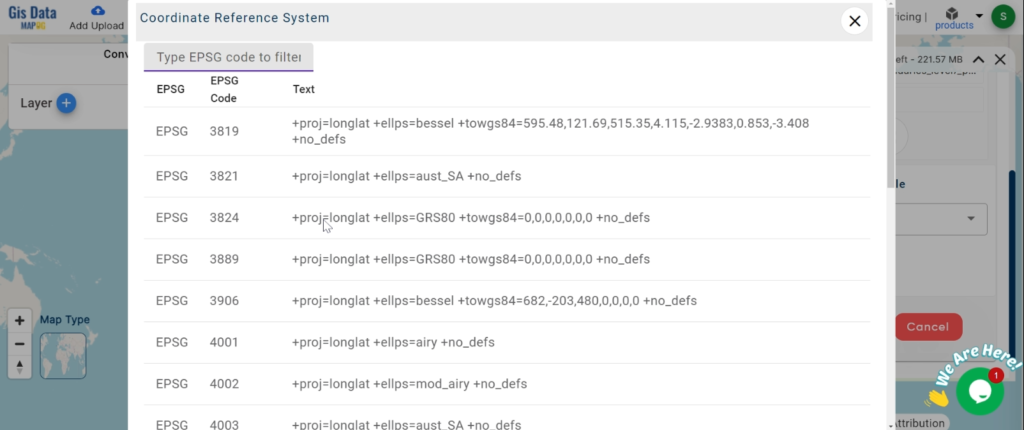
Our platform supports an extensive range of data formats, including KML, SHP, CSV, GeoJSON, Tab, SQL, Tiff, GML, KMZ, GPKZ, SQLITE, Dxf, MIF, TOPOJSON, XLSX, GPX, ODS, MID, and GPS, ensuring seamless compatibility and accessibility across different analyses.
Note:
- all data provided by MAPOG are in GCS datum EPSG:4326 WGS84 CRS (Coordinate Reference System).
- access to shapefile downloads requires logging in to the platform.
Download Data of Serbia
Serbia, nestled in the heart of the Balkans, offers a captivating blend of historical heritage and natural beauty. Known for its vibrant cities, diverse landscapes, and rich cultural traditions, Serbia is a fascinating destination for geospatial exploration.
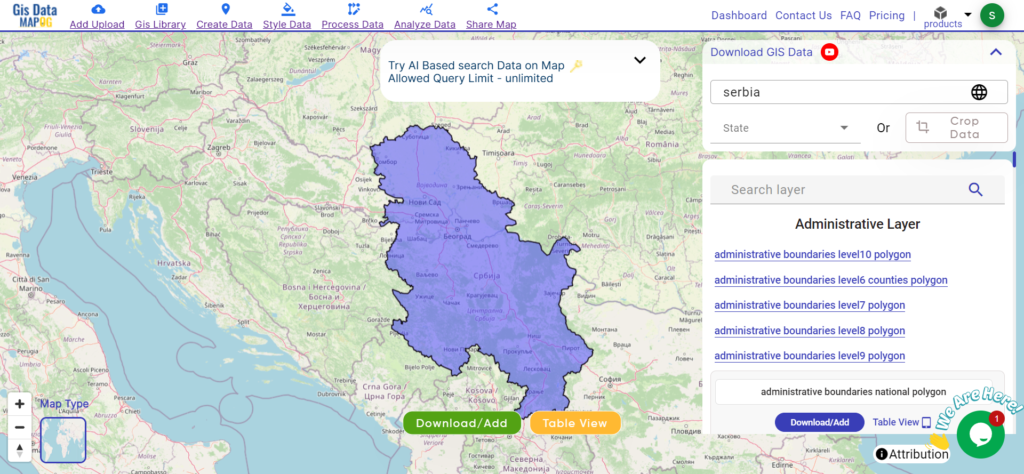
Download Serbia Province Data
Serbia is divided into distinct administrative areas, each with its own unique characteristics and governance structures. Delve into the administrative boundaries and geographic features of these divisions to gain a deeper understanding of their diversity and importance.
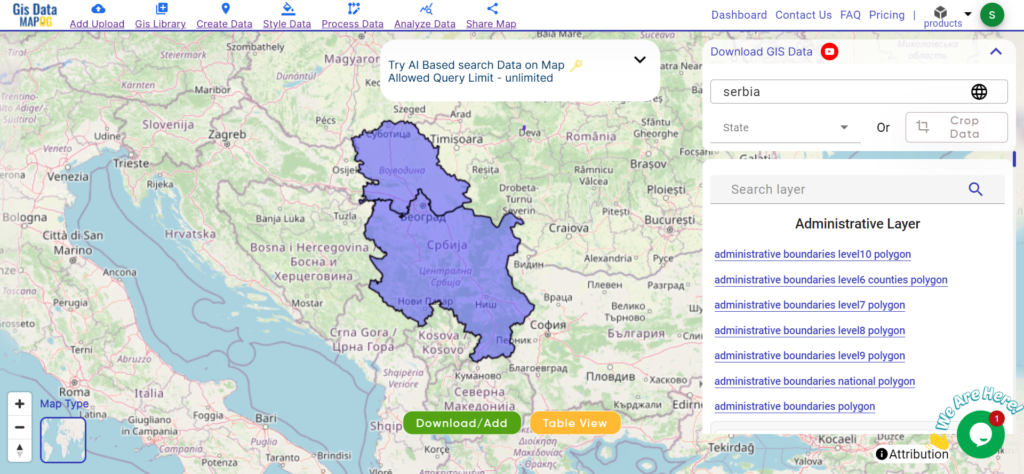
Download Serbia District Shapefile
Explore the administrative boundaries, road networks, and key geographic features of Serbia, known for its dynamic cities, historical sites, and scenic landscapes.
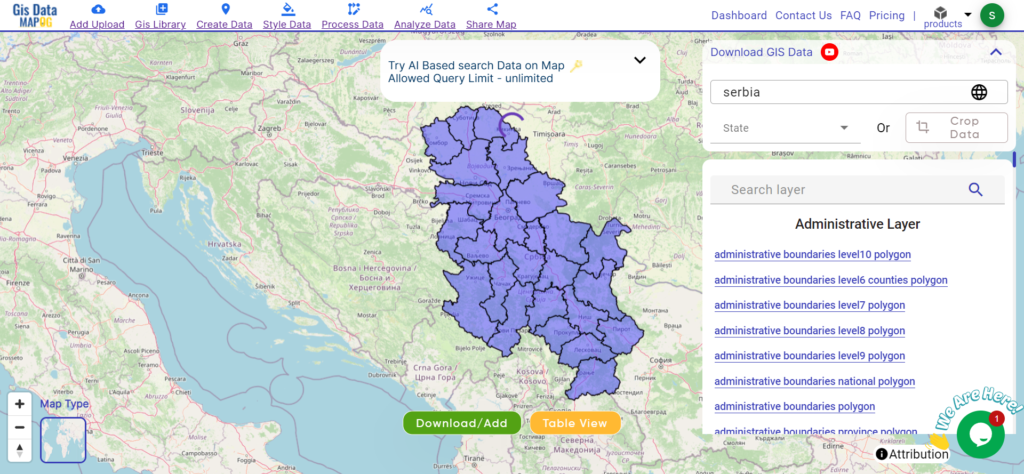
Download Serbia District Shapefile
Other GIS Data:
- Download Airport Point Data
- Download Tourism Data
- Download Conservation and Forest Data
- Download Settlement Data
Above all links are provided for GIS data of Serbia if you are looking for any specific data please write us on support@mapog.com
Download Data for the following:
- World Countries Shapefile
- Australia
- Argentina
- Austria
- Belgium
- Brazil
- Canada
- Denmark
- Fiji
- Finland
- Germany
- Greece
- India
- Indonesia
- Ireland
- Italy
- Japan
- Kenya
- Lebanon
- Madagascar
- Malaysia
- Mexico
- Mongolia
- Netherlands
- New Zealand
- Nigeria
- Papua New Guinea
- Philippines
- Poland
- Russia
- Singapore
- South Africa
- South Korea
- Spain
- Switzerland
- Tunisia
- United Kingdom Shapefile
- United States of America
- Vietnam
- Croatia
- Chile
- Norway
- Maldives
- Bhutan
- Colombia
- Libya
- Comoros
- Hungary
- Laos
- Estonia
- Iraq
- Portugal
- Azerbaijan
- Macedonia
- Romania
- Peru
- Marshall Islands
- Slovenia
- Nauru
- Guatemala
- El Salvador
- Afghanistan
- Cyprus
- Syria
- Slovakia
- Luxembourg
- Jordan
- Armenia
- Haiti And Dominican Republic
- Malta
- Djibouti
- East Timor
- Micronesia
- Morocco
- Liberia
- Kosovo
- Isle Of Man
- Paraguay
- Tokelau
- Palau
- Ile De Clipperton
- Mauritius
- Equatorial Guinea
- Tonga
- Myanmar
- Thailand
- New Caledonia
- Seychelles
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- China
- Kenya
- Kyrgyzstan
Disclaimer : If you find any shapefile data of country provided is incorrect do contact us or comment below, so that we will correct the same in our system as well we will try to correct the same in openstreetmap.