Convert GeoJSON to TopoJSON. GeoJSON is an open standard format designed for representing simple geographical features, along with their non-spatial attributes, based on JavaScript Object Notation. The need of conversion is to reduce the size of data, so that rendering of data on browser can be made faster. TopoJSON (topological geospatial data) is an extension of GeoJSON that encodes topology. Here we have explored two methods for conversion of GeoJSON to TopoJSON (i.e. online and offline).
Use Online Converter Tool – Geojson to TopoJSON MapOG
Offline Method to Convert GeoJSON to TopoJSON:
You can directly convert GeoJSON to TopoJSON with the help of topojoson-server node package manager. For using this package you need to first install node js in your system (can be installed in windows, linux based operating system or Mac).
If you have Shapefile or KML file, then you can refere this articles i.e convert kml to shapefile, convert shapefile to GeoJSON and converting shapefile to kml, so that you can generate new GeoJSON file out of other GIS format files.
Convert GeoJSON to TopoJSON – NPM method
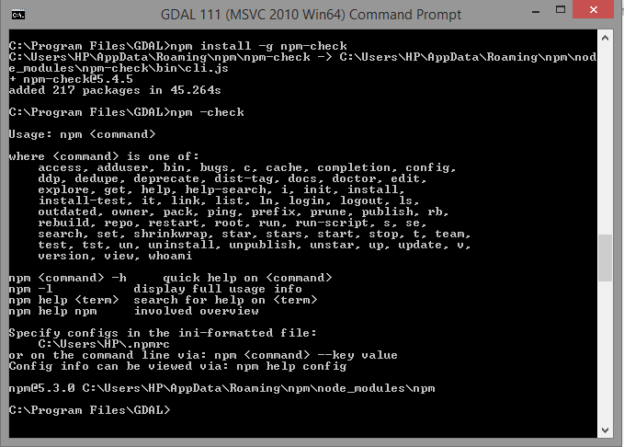
NPM (Node Package Manager) is a command-line utility that aids in package installation, version management, and dependency management or can be considered npm as a tool that helps to install another tools like topojson-server.
For this method you need to download node.js which is available https://nodejs.org/en/ here. After successful installation you need to check npm availability using command
- npm –check.
If not available use
- npm install -g npm-check
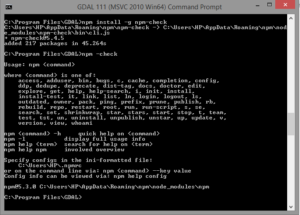
After this you need to install topojson-server for conversion of data that can be done by using
- npm install -g topojson-server
Now all setup is ready
Use geo2topo command to convert geojson data to topojson data
- geo2topo –o geo.json topo.json
Where geo.json is the geojson file i.e input file and topo.json is the file we are creating with the name topo as topo.json file i.e output file.
Here –o is output. If command doesn’t run and gives error as no such file or directory. Then specify full path for file for both input and output. It is recommended that you run this command from the same directory where geo.json file is stored.
If you don’t have any input files ready or any geojson or shapefile then you can download free GIS data format for testing this article.
Online method: Convert GeoJson to TopoJson
This is the simple and fast method. For the conversion you just need to drag the geojson file in http://mapshaper.org/ site. Then use export option to convert this data into topojson format. Map shaper website render and convert the file in the browser itself, but it you might face problem while converting a big geojson file.
I hope that this methods listed above to convert geojson to topojson would have helped you in achieving result. If you find any problem or know any other method to perform this operation and want to share with us, then do let us know by commenting below, in the box provided.